Respiratory muscle training in children and adults with neuromuscular disease
- PMID: 31487757
- PMCID: PMC6953358
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011711.pub2
Respiratory muscle training in children and adults with neuromuscular disease
Abstract
Background: Neuromuscular diseases (NMDs) are a heterogeneous group of diseases affecting the anterior horn cell of spinal cord, neuromuscular junction, peripheral nerves and muscles. NMDs cause physical disability usually due to progressive loss of strength in limb muscles, and some NMDs also cause respiratory muscle weakness. Respiratory muscle training (RMT) might be expected to improve respiratory muscle weakness; however, the effects of RMT are still uncertain. This systematic review will synthesize the available trial evidence on the effectiveness and safety of RMT in people with NMD, to inform clinical practice.
Objectives: To assess the effects of respiratory muscle training (RMT) for neuromuscular disease (NMD) in adults and children, in comparison to sham training, no training, standard treatment, breathing exercises, or other intensities or types of RMT.
Search methods: On 19 November 2018, we searched the Cochrane Neuromuscular Specialized Register, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, and Embase. On 23 December 2018, we searched the US National Institutes for Health Clinical Trials Registry (ClinicalTrials.gov), the World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, and reference lists of the included studies.
Selection criteria: We included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and quasi-RCTs, including cross-over trials, of RMT in adults and children with a diagnosis of NMD of any degree of severity, who were living in the community, and who did not need mechanical ventilation. We compared trials of RMT (inspiratory muscle training (IMT) or expiratory muscle training (EMT), or both), with sham training, no training, standard treatment, different intensities of RMT, different types of RMT, or breathing exercises.
Data collection and analysis: We followed standard Cochrane methodological procedures.
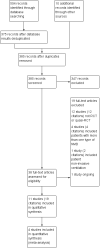
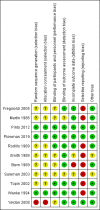
Main results: We included 11 studies involving 250 randomized participants with NMDs: three trials (N = 88) in people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS; motor neuron disease), six trials (N = 112) in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), one trial (N = 23) in people with Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) or limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, and one trial (N = 27) in people with myasthenia gravis.Nine of the trials were at high risk of bias in at least one domain and many reported insufficient information for accurate assessment of the risk of bias. Populations, interventions, control interventions, and outcome measures were often different, which largely ruled out meta-analysis. All included studies assessed lung capacity, our primary outcome, but four did not provide data for analysis (1 in people with ALS and three cross-over studies in DMD). None provided long-term data (over a year) and only one trial, in ALS, provided information on adverse events. Unscheduled hospitalisations for chest infection or acute exacerbation of chronic respiratory failure were not reported and physical function and quality of life were reported in one (ALS) trial.Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)Three trials compared RMT versus sham training in ALS. Short-term (8 weeks) effects of RMT on lung capacity in ALS showed no clear difference in the change of the per cent predicted forced vital capacity (FVC%) between EMT and sham EMT groups (mean difference (MD) 0.70, 95% confidence interval (CI) -8.48 to 9.88; N = 46; low-certainty evidence). The mean difference (MD) in FVC% after four months' treatment was 10.86% in favour of IMT (95% CI -4.25 to 25.97; 1 trial, N = 24; low-certainty evidence), which is larger than the minimal clinically important difference (MCID, as estimated in people with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis). There was no clear difference between IMT and sham IMT groups, measured on the Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Rating Scale (ALFRS; range of possible scores 0 = best to 40 = worst) (MD 0.85, 95% CI -2.16 to 3.85; 1 trial, N = 24; low-certainty evidence) or quality of life, measured on the EuroQol-5D (0 = worst to 100 = best) (MD 0.77, 95% CI -17.09 to 18.62; 1 trial, N = 24; low-certainty evidence) over the medium term (4 months). One trial report stated that the IMT protocol had no adverse effect (very low-certainty evidence).Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)Two DMD trials compared RMT versus sham training in young males with DMD. In one study, the mean post-intervention (6-week) total lung capacity (TLC) favoured RMT (MD 0.45 L, 95% CI -0.24 to 1.14; 1 trial, N = 16; low-certainty evidence). In the other trial there was no clear difference in post-intervention (18 days) FVC between RMT and sham RMT (MD 0.16 L, 95% CI -0.31 to 0.63; 1 trial, N = 20; low-certainty evidence). One RCT and three cross-over trials compared a form of RMT with no training in males with DMD; the cross-over trials did not provide suitable data. Post-intervention (6-month) values showed no clear difference between the RMT and no training groups in per cent predicted vital capacity (VC%) (MD 3.50, 95% CI -14.35 to 21.35; 1 trial, N = 30; low-certainty evidence).Becker or limb-girdle muscular dystrophyOne RCT (N = 21) compared 12 weeks of IMT with breathing exercises in people with Becker or limb-girdle muscular dystrophy. The evidence was of very low certainty and conclusions could not be drawn.Myasthenia gravisIn myasthenia gravis, there may be no clear difference between RMT and breathing exercises on measures of lung capacity, in the short term (TLC MD -0.20 L, 95% CI -1.07 to 0.67; 1 trial, N = 27; low-certainty evidence). Effects of RMT on quality of life are uncertain (1 trial; N = 27).Some trials reported effects of RMT on inspiratory and/or expiratory muscle strength; this evidence was also of low or very low certainty.
Authors' conclusions: RMT may improve lung capacity and respiratory muscle strength in some NMDs. In ALS there may not be any clinically meaningful effect of RMT on physical functioning or quality of life and it is uncertain whether it causes adverse effects. Due to clinical heterogeneity between the trials and the small number of participants included in the analysis, together with the risk of bias, these results must be interpreted very cautiously.
Conflict of interest statement
ISS: none known. RP: none known. IGA: none known. AMF: none known. GAFF: none known. He is the author of a trial included in this Cochrane Review (Fregonezi 2005). METDJ: none known. He has received lecture fees from Sociedade Brasileira de Neurofisiologia Clínica. SRHL: none known. GMHF: none known.
Figures































Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011711
Similar articles
-
Interventions for promoting physical activity in people with neuromuscular disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 May 24;5(5):CD013544. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013544.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34027632 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-based therapies for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/motor neuron disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Dec 19;12(12):CD011742. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011742.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31853962 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for preventing and treating cardiac complications in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy and X-linked dilated cardiomyopathy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 16;10(10):CD009068. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009068.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30326162 Free PMC article.
-
Strength training and aerobic exercise training for muscle disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Dec 6;12(12):CD003907. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003907.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31808555 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological interventions for improving adherence to inhaled therapies in people with cystic fibrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Mar 29;3(3):CD013766. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013766.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36989170 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Linking Findings to the Physical Therapy Clinic.Phys Ther. 2020 Oct 30;100(11):2035-2048. doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzaa140. Phys Ther. 2020. PMID: 32737968 Free PMC article.
-
Rehabilitation in patients with cerebellar ataxias.Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2022 Mar;80(3):306-315. doi: 10.1590/0004-282X-ANP-2021-0065. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2022. PMID: 35239817 Free PMC article.
-
The role of lung volume recruitment therapy in neuromuscular disease: a narrative review.Front Rehabil Sci. 2023 Jul 26;4:1164628. doi: 10.3389/fresc.2023.1164628. eCollection 2023. Front Rehabil Sci. 2023. PMID: 37565183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Respiratory failure and sleep-disordered breathing in late-onset Pompe disease: a narrative review.J Thorac Dis. 2020 Oct;12(Suppl 2):S235-S247. doi: 10.21037/jtd-cus-2020-007. J Thorac Dis. 2020. PMID: 33214927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Respiratory Muscle Strength Training in Parkinson's Disease-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 May 21;13(10):1214. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13101214. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40428050 Free PMC article. Review.
References
References to studies included in this review
Fregonezi 2005 {published data only}
-
- Fregonezi GA, Guell R, Pradas J, Casan P. Effects of inspiratory muscle training program in generalized myasthenia gravis. European Respiratory Journal 2003;22(Suppl 45):2729.
-
- Fregonezi GA, Resqueti VR, Güell R, Pradas J, Casan P. Effects of 8‐week, interval‐based inspiratory muscle training and breathing retraining in patients with generalized myasthenia gravis. Chest 2005;128(3):1524‐30. [PUBMED: 16162753] - PubMed
Martin 1986 {published data only}
-
- Martin AJ, Stern L, Yeates J, Lepp D, Little J. Respiratory muscle training in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 1986;28(3):314‐8. - PubMed
Pinto 2012 {published data only}
-
- Pinto S, Carvalho M. Respiratory exercises in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (reals). Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis 2009;10:59. [EMBASE: 70078384]
-
- Pinto S, Swash M, Carvalho M. Respiratory exercise in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis 2012;13(1):33‐43. [PUBMED: 22214352] - PubMed
-
- Pinto S, Carvalho M. Can inspiratory muscle training increase survival in early‐affected amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients?. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Degeneration 2013;14(2):124‐6. [PUBMED: 23035780] - PubMed
Plowman 2019 {published data only}
-
- Plowman E, Tabor L, Rosado MK, Robison R, Gaziano J, Richter J, et al. A randomized sham control trial of EMST on bulbar function. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Degeneration 2015;16(Suppl 1):44. [DOI: 10.3109/21678421.2015.1089039/0065] - DOI
-
- Plowman EK, Rosado M, Tabor L, Turner K, Gaziano J, Richter J, et al. Impact of expiratory muscle strength training on bulbar function in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: updates from a randomized sham‐controlled clinical trial. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Degeneration 2014;15:206.
Rodillo 1989 {published data only}
Smith 1988 {published data only}
-
- Smith PE, Coakley JH, Edwards RH. Respiratory muscle training in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Muscle & Nerve 1988;11(7):784‐7. - PubMed
Stern 1989 {published data only}
-
- Stern LM, Martin AJ, Jones N, Garrett R, Yeates J. Training inspiratory resistance in Duchenne dystrophy using adapted computer games. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 1993;31(4):494‐500. - PubMed
Suleman 2003 {published data only}
-
- Suleman M, Whitely A, Kinnear W. Expiratory muscle training in motor neurone disease [Abstract]. Thorax 2003;58(Suppl 3):iii77‐8.
Topin 2002 {published data only}
-
- Topin N, Matecki S, Bris S, Rivier F, Echenne B, Prefaut C, et al. Dose‐dependent effect of individualized respiratory muscle training in children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neuromuscular Disorders 2002;12(6):576‐83. [PUBMED: 12117483] - PubMed
Wanke 1994 {published data only}
-
- Merkle M, Wanke TH, Formanek D, Lahrmann H, Toifl K, Zwick H. Inspiratory muscle training in patients with neuromuscular disease [abstract]. European Respiratory Journal 1993;6(Suppl 17):310S.
-
- Ungar D, Gössler R, Toifl K, Wanke T. Innovative respiratory muscle training for patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy‐a psychological evaluation. Wiener Medizinische Wochenschrift 1996;146(9‐10):213‐6. [PUBMED: 9012219] - PubMed
-
- Wanke T, Toifl K, Merkle M, Formanek D, Lahrmann H, Zwick H. Inspiratory muscle training in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Chest 1994;105(2):475‐82. [PUBMED: 8306750] - PubMed
-
- Wild M, Wanke T, Lahrmann H, Merkle M, Toifl K, Zwick H. Training of the respiratory musculature in muscle dystrophy Duchenne. Atemwegs ‐ und Lungenkrankheiten 1995;21:478.
Yeldan 2008 {published data only}
-
- Yeldan I, Gurses HN, Yuksel H. Comparison study of chest physiotherapy home training programmes on respiratory functions in patients with muscular dystrophy. Clinical Rehabilitation 2008;22(8):741‐8. [PUBMED: 18678574] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abe 1998 {published data only}
-
- Abe K, Matsuo Y, Kadekawa J, Inoue S, Yanagihara T. Respiratory training for patients with myotonic dystrophy. Neurology 1998;51(2):641‐2. - PubMed
Aslan 2014 {published data only}
-
- Aslan GK, Gurses HN, Issever H, Kiyan E. Effects of respiratory muscle training on pulmonary functions in patients with slowly progressive neuromuscular disease: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2014;28(6):573‐81. - PubMed
Cheah 2009 {published data only}
-
- Cheah B, Boland R, Brodaty N, Zoing M, Jeffery S, McKenzie D, et al. "Inspirational" ‐ Inspiratory muscle training in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. 20th International Symposium on ALS/MND; 2009 Dec 8‐10; Berlin, Germany. 2009. - PubMed
-
- Cheah BC, Boland RA, Brodaty NE, Zoing MC, Jeffery SE, McKenzie DK, et al. INSPIRATIonAL ‐ INSPIRAtory muscle training in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis 2009;10(5‐6):384‐92. - PubMed
DiMarco 1985 {published data only}
-
- DiMarco AF, Kelling JS, DiMarco MS, Jacobs I, Shields R, Altose MD. The effects of inspiratory resistive training on respiratory muscle function in patients with muscular dystrophy. Muscle & Nerve 1985;8(4):284‐90. - PubMed
Estrup 1986 {published data only}
-
- Estrup C, Lyager S, Noeraa N, Olsen C. Effect of respiratory muscle training in patients with neuromuscular diseases and in normals. Respiration 1986;50(1):36‐43. - PubMed
Fregonezi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Fregonezi GA, Araujo TL, Azevedo IG, Severino FG, Dias FA, Bruno SS, et al. Effects of respiratory muscle training on strength and heart rate variability in myotonic dystrophy patients. Chest 2010;138(4):920A.
Gozal 1999 {published data only}
-
- Gozal D, Thiriet P. Respiratory muscle training in neuromuscular disease: long‐term effects on strength and load perception. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 1999;31(11):1522‐7. - PubMed
Gross 1993 {published data only}
-
- Gross D, Meiner Z. The effect of ventilatory muscle training on respiratory function and capacity in ambulatory and bed‐ridden patients with neuromuscular disease. Monaldi Archives for Chest Disease 1993;48(4):322‐6. - PubMed
Koessler 2001 {published data only}
-
- Koessler W, Wanke T, Winkler G, Nader A, Toifl K, Kurz H, et al. 2 Years' experience with inspiratory muscle training in patients with neuromuscular disorders. Chest 2001;120(3):765‐9. - PubMed
Litchke 2008 {published data only}
Núñez 2014 {published data only}
Plowman 2016 {published data only}
Rassler 2007 {published data only}
-
- Rassler B, Hallebach G, Kalischewski P, Baumann I, Schauer J, Spengler CM. The effect of respiratory muscle endurance training in patients with myasthenia gravis. Neuromuscular Disorders 2007;17(5):385‐91. - PubMed
Rassler 2011 {published data only}
Raßler 2014 {published data only}
-
- Raßler B, Hallebach S, Freitag S, Baumann I, Kalischewski P. Long‐term respiratory muscle endurance training in patients with myasthenia gravis. Acta Physiologica 2014;210(Suppl 695):138‐9. [EMBASE: 71389711]
Weiner 1998 {published data only}
-
- Weiner P, Gross D, Meiner Z, Ganem R, Weiner M, Zamir D, et al. Respiratory muscle training in patients with moderate to severe myasthenia gravis. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 1998;25(3):236‐41. - PubMed
Zupan 2002 {published data only}
-
- Zupan A, Praznikar A, Sardoc M. Inspiratory versus expiratory muscle training in children with neuromuscular diseases. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2002;199(Suppl 1):S32.
References to ongoing studies
NCT02710110 {published data only}
-
- NCT02710110. Respiratory strength training in persons with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) [The impact of respiratory strength training in individuals with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02710110 (first posted 16 March 2016). [NCT02710110]
Additional references
Aboussouan 2009
-
- Aboussouan LS. Mechanisms of exercise limitation and pulmonary rehabilitation for patients with neuromuscular disease. Chronic Respiratory Disease 2009;6(4):231‐49. - PubMed
Abresch 2012
-
- Abresch RT, Carter GT, Han JJ, McDonald CM. Exercise in neuromuscular diseases. Physical Medicine Rehabilitation Clinics North America 2012;23(3):653‐73. - PubMed
Alonso 1995
-
- Alonso J, Prieto L, Antó JM. The Spanish version of the SF‐36 Health Survey (the SF‐36 health questionnaire): an instrument for measuring clinical results [La versión española del SF‐36 Health Survey (Cuestionario de Salud SF‐36): un instrumentopara la medida de los resultados clínicos]. Medicine Clinica 1995;104(20):771‐6. - PubMed
Ambrosino 2009
-
- Ambrosino N, Carpene N, Gherardi M. Chronic respiratory care for neuromuscular diseases in adults. European Respiratory Journal 2009;34(2):444‐51. - PubMed
Anziska 2013
-
- Anziska Y, Sternberg A. Exercise in neuromuscular disease. Muscle & Nerve 2013;48(1):3‐20. - PubMed
Benditt 2006
-
- Benditt JO. The neuromuscular respiratory system: physiology, pathophysiology, and a respiratory care approach to patients. Respiratory Care 2006;51(8):829‐39. - PubMed
Berlowitz 2013
Brooks 2000
-
- Brooks BR, Miller RG, Swash M, Munsat TL, World Federation of Neurology Research Group on Motor Neuron Diseases. El Escorial revisited: revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Sclerosis and Other Motor Neuron Disorders 2000;1(5):293‐9. - PubMed
Cedarbaum 1997
-
- Cedarbaum JM, Stambler N. Performance of the Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Rating Scale (ALSFRS) in multicenter clinical trials. Journal of Neurological Sciences 1997;152(Suppl 1):S1‐9. - PubMed
Cedarbaum 1999
-
- Cedarbaum JM, Stambler N, Malta E, Fuller C, Thurmond B, Nakanishi A. The ALSFRS‐R: a revised ALS functional rating scale that incorporates assessments of respiratory function. BDNF ALS Study Group (Phase III). Journal of the Neurological Sciences 1999;169(1‐2):13‐21. - PubMed
CONSORT 2010
-
- Moher D, Hopewell S, Schulz KF, Montori V, Gøtzsche PC, Devereaux PJ, et al. CONSORT 2010 Statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2010;63(8):834‐40. - PubMed
Cup 2007
-
- Cup EH, Pieterse AJ, Broek‐Pastoor JM, Munneke M, Engelen BG, Hendricks HT, et al. Exercise therapy and other types of physical therapy for patients with neuromuscular diseases: a systematic review. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2007;88(11):1452‐64. - PubMed
D'Angelo 2011
-
- D'Angelo MG, Romei M, Lo Mauro A, Marchi E, Gandossini S, Bonato S. Respiratory pattern in an adult population of dystrophic patients. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2011;306(1‐2):54‐61. - PubMed
de Godoy 2012
-
- Godoy VC, Lanzillotta P. Respiratory muscle training in Becker's muscular dystrophy ‐ critical literature review [Treinamento muscular respiratório na distrofia muscular de Becker ‐ revisão crítica de literatura]. Revista Neurociências 2012;20(1):138‐43.
de la Loge 2016
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JP, Altman DG, editor(s), on behalf of the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
du Bois 2011
-
- du Bois RM, Weycker D, Albera C, Bradford WZ, Costabel U, Kartashov A, et al. Forced vital capacity in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: test properties and minimal clinically important difference. American Journal of Respiratory Critical Care Medicine 2011;184(12):1382‐9. - PubMed
Eagle 2002
-
- Eagle M. Report on the Muscular Dystrophy Campaign workshop: exercise in neuromuscular diseases Newcastle, January 2002. Neuromuscular Disorders 2002;12(10):975‐83. - PubMed
Eidenberger 2014
-
- Eidenberger M, Nowotny S. Inspiratory muscle training in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a systematic review. NeuroRehabilitation 2014;35(3):349‐61. - PubMed
Emery 1991
-
- Emery AE. Population frequencies of inherited neuromuscular diseases ‐ a world survey. Neuromuscular Disorders 1991;1(1):19‐29. - PubMed
Emery 1994
-
- Emery AE, editor. Diagnostic Criteria for Neuromuscular Disorders. Baarn, The Netherlands: European Neuromuscular Centre, 1994. [ISBN: ISBN 90 261 0719 6, 72 pp]
Enright 2011
-
- Enright SJ, Unnithan VB. Effect of inspiratory muscle training intensities on pulmonary function and work capacity in people who are healthy: a randomized controlled trial. Physical Therapy 2011;91(6):894‐905. - PubMed
Epstein 1994
-
- Epstein SK. An overview of respiratory muscle function. Clinics in Chest Medicine 1994;15(4):619‐39. - PubMed
Estournet‐Mathiaud 2003
-
- Estournet‐Mathiaud B. Respiratory complications of neuromuscular diseases [Complications respiratoires des maladies neuromusculaires]. In: Dutau G, Labbé A editor(s). Pneumologie de l'Enfant. 2nd Edition. Paris: Arnette, Blackwell, 2003:273‐83.
Faber 2014
Ferreira 2016
-
- Ferreira GD, Costa AC, Plentz RD, Coronel CC, Sbruzzi G. Respiratory training improved ventilatory function and respiratory muscle strength in patients with multiple sclerosis and lateral amyotrophic sclerosis: systematic review and meta‐analysis. Physiotherapy 2016;102(3):221‐8. - PubMed
Finder 2004
-
- Finder JD, Birnkrant D, Carl J, Farber HJ, Gozal D, Iannaccone ST, et al. American Thoracic Society. Respiratory care of the patient with Duchenne muscular dystrophy: ATS Consensus Statement. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2004; Vol. 170, issue 4:456‐65. - PubMed
Fitting 2006
-
- Fitting FW. Sniff nasal inspiratory pressure: simple or too simple?. European Respiratory Journal 2006;27(5):881‐3. - PubMed
GRADEpro GDT 2015 [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime). GRADEpro GDT. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015.
HajGhanbari 2013
-
- HajGhanbari B, Yamabayashi C, Buna TR, Coelho JD, Freedman KD, Morton TA, et al. Effects of respiratory muscle training on performance in athletes: a systematic review with meta‐analysis. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research 2013;27(6):1643‐63. - PubMed
Hannan 2014
-
- Hannan LM, Dominelli GS, Chen YW, Darlene Reid W, Road J. Systematic review of non‐invasive positive pressure ventilation for chronic respiratory failure. Respiratory Medicine 2014;108(2):229‐43. - PubMed
Hapke 1972
-
- Hapke EJ, Meek JC, Jacobs J. Pulmonary function in progressive muscular dystrophy. Chest 1972;61(1):41‐7. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Hill 2004
-
- Hill K, Jenkins SC, Hillman DR, Eastwood PR. Dyspnoea in COPD: can inspiratory muscle training help?. Australian Journal of Physiotherapy 2004;50(3):169‐80. - PubMed
Hoffman 2002
-
- Hoffman J. Physiological Aspects of Sport Training and Performance. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics, 2002.
Huang 2011
-
- Huang CH, Yang GG, Wu YT, Lee CW. Comparison of inspiratory muscle strength training effects between older subjects with and without chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association 2011;110(8):518‐26. - PubMed
Human 2017
-
- Human A, Corten L, Jelsma J, Morrow B. Inspiratory muscle training for children and adolescents with neuromuscular diseases: A systematic review. Neuromuscular Disorders 2017;27(6):503‐17. - PubMed
Illi 2012
-
- Illi SK, Held U, Frank I, Spengler CM. Effect of respiratory muscle training on exercise performance in healthy individuals: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Sports Medicine 2012;42(8):707‐24. - PubMed
Inkley 1974
-
- Inkley SR, Oldenburg FC, Vignos PJ Jr. Pulmonary function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy related to stage of disease. The American Journal of Medicine 1974;56(3):297‐306. - PubMed
Jones 1991
-
- Jones PW, Quirk FH, Baveystock CM. The St George's Respiratory Questionnaire. Respiratory Medicine 1991;85(suppl B):25‐31. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Jones 1992
-
- Jones PW, Quirk FH, Baveystock CM, Littlejohns P. A self‐complete measure of health status for chronic airflow limitation. The St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire. American Review of Respiratory Disease 1992;145(6):1321‐7. - PubMed
Jones 2002
-
- Jones PW. Interpreting thresholds for a clinically significant change in health status in asthma and COPD. European Respiratory Journal 2002;19(3):398‐404. - PubMed
Jones 2005
-
- Jones PW. St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire: MCID. COPD 2005;2(1):75‐9. - PubMed
Landrigan 2005
-
- Landrigan PJ, Garg A. Children are not little adults. In: Pronczuk‐Garbino J editor(s). Children's Health and the Environment: a global perspective: a resource manual for the health sector. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2005:3‐16.
Leith 1976
-
- Leith DE, Bradley M. Ventilatory muscle strength and endurance training. Journal of Applied Physiology 1976;41(4):508‐16. - PubMed
MacDonald 2002
-
- MacDonald CM. Physical activity, health impairments, and disability in neuromuscular disease. Journal of American Journal of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2002;81(11 Suppl):S108‐20. - PubMed
McConnell 2009
-
- McConnell AK. Respiratory muscle training as an ergogenic aid. Journal of Exercise Science & Fitness 2009;7(2):S18‐S27.
McCool 1995
-
- McCool FD, Tzelepis GE. Inspiratory muscle training in the patient with neuromuscular disease. Physical Therapy 1995;75(11):1006‐14. - PubMed
McDonald 2012
Misuri 2000
-
- Misuri G, Lanini B, Gigliotti F, Iandelli I, Pizzi A, Bertolini MG. Mechanism of CO2 retention in patients with neuromuscular disease. Chest 2000;117(2):447‐53. - PubMed
Moher 2009
Moodie 2011
Nici 2006
-
- Nici L, Donner C, Wouters E, Zuwallack R, Ambrosino N, Bourbeau J, et al. ATS/ERS Pulmonary Rehabilitation Writing Committee. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement on pulmonary rehabilitation. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2006;173(12):1390‐413. - PubMed
Osserman 1971
-
- Osserman KE, Genkins G. Studies in myasthenia gravis: review of a twenty‐year experience in over 1200 patients. The Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine 1971;38(6):497‐537. - PubMed
Page 2016
Park 2010
Paschoal 2007
-
- Paschoal IA, Villalba WO, Pereira MC. Chronic respiratory failure in patients with neuromuscular diseases: diagnosis and treatment [Insuficiência respiratória crônica nas doenças neuromusculares: diagnóstico e tratamento]. Jornal Brasileiro de Pneumologia 2007;33(1):81‐92. - PubMed
Pellegrino 2005
-
- Pellegrino R, Viegi G, Brusasco V, Crapo RO, Burgos F, Casaburi R, et al. Interpretative strategies for lung function tests. European Respiratory Journal 2005;26(5):948‐68. - PubMed
Pine 2005
-
- Pine M, Watsford M. Specific respiratory muscle training for athletic performance. Sports Coach 2005;27(4):1‐4.
Pinto 2014
-
- Pinto S, Carvalho M. Breathing new life into treatment advances for respiratory failure in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Neurodegenerative Disease Management 2014;4(1):83‐102. - PubMed
Pollock 2013
-
- Pollock RD, Rafferty GF, Moxham J, Kalra L. Respiratory muscle strength and training in stroke and neurology: a systematic review. International Journal of Stroke 2013;8(2):124‐30. - PubMed
Pontes 2012
-
- Pontes JF, Ferreira GM, Fregonezi GA, Sena‐Evangelista KC, Dourado ME Jr. Respiratory muscle strength, nutritional and postural profile in children with neuromuscular diseases [Força muscular respiratória e perfil postural e nutricional em crianças com doenças neuromusculares]. Fisioterapia em Movimento 2012;25(2):253‐61.
Pustavoitau 2008
-
- Pustavoitau A, Stevens RD. Mechanisms of neurologic failure in critical illness. Critical Care Clinics 2008;24(1):1‐24. - PubMed
Rabin 2001
-
- Rabin R, Charro F. EQ‐5D: a measure of health status from the EuroQol Group. Annals of Medicine 2001;33(5):337‐43. - PubMed
Radunovic 2017
Ramirez‐Sarmiento 2008
-
- Ramirez‐Sarmiento A, Orozco‐Levi M. Pulmonary rehabilitation should be prescribed in the same way medications are prescribed. Archivos de Bronconeumología 2008;44(3):119‐21. - PubMed
Reed 2002
-
- Reed UC. Neuromuscular diseases [Doenças neuromusculares]. Jornal de Pediatria 2002;78(Suppl 1):S89‐103. - PubMed
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Reyes 2013
-
- Reyes A, Ziman M, Nosaka K. Respiratory muscle training for respiratory deficits in neurodegenerative disorders: a systematic review. Chest 2013;143(5):1386‐94. - PubMed
Rezania 2012
-
- Rezania K, Goldenberg FD, White S. Neuromuscular disorders and acute respiratory failure: diagnosis and management. Neurologic Clinics 2012;30(1):161–85. - PubMed
Riebe 2014
-
- Riebe D. Exercise prescription. In: Pescatello LS editor(s). ACSM's Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription. 9th Edition. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Health, 2014:161‐93.
Rietberg 2017
Romer 2003
-
- Romer LM, McConnell AK. Specificity and reversibility of inspiratory muscle training. Medicine and Science in Sports Exercise 2003;35(2):237‐44. - PubMed
Sander 2000
-
- Sander M, Chavoshan B, Harris SA, Iannaccone ST, Stull JT, Thomas GD, et al. Functional muscle ischemia in neuronal nitric oxide synthase‐deficient skeletal muscle of children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the Unites States of America 2000;97(25):13818‐23. - PMC - PubMed
Sartori 2008
-
- Sartori R, Barbi E, Poli F, Ronfani L, Marchetti F, Amaddeo A, et al. Respiratory training with a specific device in cystic fibrosis: a prospective study. Journal of Cystic Fibrosis 2008;7(4):313‐9. - PubMed
Savović 2012
-
- Savović J, Jones H, Altman D, Harris R, Jűni P, Pildal J, et al. Influence of reported study design characteristics on intervention effect estimates from randomised controlled trials: combined analysis of meta‐epidemiological studies. Health Technology Assessment 2012;16(35):1–82. - PubMed
Schünemann 2013
-
- Schünemann H, Brożek J, Guyatt G, Oxman A, editor(s). Handbook for grading the quality of evidence and the strength of recommendations using the GRADE approach (updated October 2013). GRADE Working Group, 2013. Available from gdt.guidelinedevelopment.org/app/handbook/handbook.html.
Thomas 2013
Timpani 2017
Tzelepis 1994
-
- Tzelepis GE, Vega DL, Cohen ME, Fulambarker AM, Patel KK, McCool FD. Pressure‐flow specificity of inspiratory muscle training. Journal of Applied Physiology 1994;77(2):795‐801. - PubMed
Tzelepis 1999
-
- Tzelepis GE, Kasas V, McCool FD. Inspiratory muscle adaptations following pressure or flow training in humans. European Journal of Applied Physiology 1999;79(6):467‐71. - PubMed
Van Houtte 2006
-
- Houtte S, Vanlandewijck Y, Gosselink R. Respiratory muscle training in persons with spinal cord injury: a systematic review. Respiratory Medicine 2006;100(11):1886‐95. - PubMed
Vandervelde 2009
-
- Vandervelde L, Bergh PY, Goemans N, Thonnard JL. Activity limitations in patients with neuromuscular disorders: a responsiveness study of the ACTIVLIM questionnaire. Neuromuscular Disorders 2009;19:99‐103. - PubMed
Ware 1992
-
- Ware JEJ, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36‐Item Short‐Form Health Survey (SF‐36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Medical Care 1992;30(6):473‐83. - PubMed
Wijdicks 2009
-
- Wijdicks EF. Generalized weakness in the intensive care unit. Neurological Complications of Critical Illness. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2009:59‐74.
Winkler 2000
-
- Winkler G, Zifko U, Nader A, Frank W, Zwick H, Toifl K, et al. Dose‐dependent effects of inspiratory muscle training in neuromuscular disorders. Muscle & Nerve 2000;23(8):1257‐60. - PubMed
Wirth 1999
-
- Wirth B, Herz M, Wetter A, Moskau S, Hahnen E, Rudnik‐Schöneborn S, et al. Quantitative analysis of survival motor neuron copies: identification of subtle SMN1 mutations in patients with spinal muscular atrophy, genotype‐phenotype correlation, and implications for genetic counseling. American Journal of Human Genetics 1999;64(5):1340‐56. - PMC - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

