Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Diseases: Still a Therapeutic Target?
- PMID: 31487802
- PMCID: PMC6769522
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11092090
Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Diseases: Still a Therapeutic Target?
Abstract
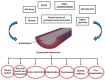
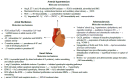
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are complex entities with heterogenous pathophysiologic mechanisms and increased oxidative stress has been viewed as one of the potential common etiologies. A fine balance between the presence of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidants is essential for the proper normal functioning of the cell. A basal concentration of ROS is indispensable for the manifestation of cellular functions, whereas excessive levels of ROS cause damage to cellular macromolecules such as DNA, lipids and proteins, eventually leading to necrosis and apoptotic cell death. CVD is the main cause of death worldwide with several conditions being affected by oxidative stress. Increased ROS lead to decreased nitric oxide availability and vasoconstriction, promoting arterial hypertension. ROS also negatively influence myocardial calcium handling, causing arrhythmia, and augment cardiac remodeling by inducing hypertrophic signaling and apoptosis. Finally, ROS have also been shown to promote atherosclerotic plaque formation. This review aims at giving an introduction into oxidative stress in CVD, with special focus on endothelial dysfunction, and then examining in detail the role of oxidative stress in the most prevalent of these diseases. Finally, potential nutraceuticals and diets that might be beneficial in diminishing the burden of oxidative stress in CVD are presented.
Keywords: antioxidants; cardiovascular diseases; nutraceuticals; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

