MTA1-Dependent Anticancer Activity of Gnetin C in Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 31487842
- PMCID: PMC6770780
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11092096
MTA1-Dependent Anticancer Activity of Gnetin C in Prostate Cancer
Abstract
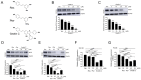
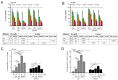
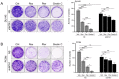
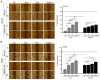
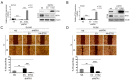
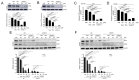
The overexpression of metastasis-associated protein 1 (MTA1) in prostate cancer (PCa) contributes to tumor aggressiveness and metastasis. We have reported the inhibition of MTA1 by resveratrol and its potent analog pterostilbene in vitro and in vivo. We have demonstrated that pterostilbene treatment blocks the progression of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and adenocarcinoma in mouse models by inhibiting MTA1 expression and signaling. In the current study, we investigated the MTA1 targeted anticancer effects of Gnetin C, a resveratrol dimer, in comparison with resveratrol and pterostilbene. Using DU145 and PC3M PCa cells, we found that Gnetin C downregulates MTA1 more potently than resveratrol and pterostilbene. Further, Gnetin C demonstrated significant MTA1-mediated inhibitory effect on cell viability, colony formation, and migration, while showing a more potent induction of cell death than resveratrol or pterostilbene. In addition, we identified Gnetin C-induced substantial ETS2 (erythroblastosis E26 transformation-specific 2) downregulation, which is not only MTA1-dependent, but is also independent of MTA1 as a possible mechanism for the superior anticancer efficacy of Gnetin C in PCa. Together, these findings underscore the importance of novel potent resveratrol dimer, Gnetin C, as a clinically promising agent for the future development of chemopreventive and possibly combinatorial therapeutic approaches in PCa.
Keywords: ETS2; Gnetin C; MTA1; prostate cancer; pterostilbene; resveratrol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Therapeutic Potential of Gnetin C in Prostate Cancer: A Pre-Clinical Study.Nutrients. 2020 Nov 26;12(12):3631. doi: 10.3390/nu12123631. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33255879 Free PMC article.
-
Gnetin C in Cancer and Other Diseases: What Do We Know So Far?Nutrients. 2025 Feb 28;17(5):863. doi: 10.3390/nu17050863. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40077738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pterostilbene acts through metastasis-associated protein 1 to inhibit tumor growth, progression and metastasis in prostate cancer.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e57542. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057542. Epub 2013 Mar 1. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23469203 Free PMC article.
-
Metastasis-associated protein 1-mediated antitumor and anticancer activity of dietary stilbenes for prostate cancer chemoprevention and therapy.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 May;80:107-117. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.02.012. Epub 2020 Feb 29. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 32126261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting MTA1/HIF-1α signaling by pterostilbene in combination with histone deacetylase inhibitor attenuates prostate cancer progression.Cancer Med. 2017 Nov;6(11):2673-2685. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1209. Epub 2017 Oct 10. Cancer Med. 2017. PMID: 29024573 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic exploration of bioactive constituents in Gnetum gnemon for GPCR-related cancer treatment through network pharmacology and molecular docking.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 28;14(1):25738. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75240-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39468096 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Gnetin C in Prostate Cancer: A Pre-Clinical Study.Nutrients. 2020 Nov 26;12(12):3631. doi: 10.3390/nu12123631. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33255879 Free PMC article.
-
Gnetin C in Cancer and Other Diseases: What Do We Know So Far?Nutrients. 2025 Feb 28;17(5):863. doi: 10.3390/nu17050863. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40077738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of metastasis-associated protein 1 (MTA1) as a new molecular marker for canine urothelial carcinoma.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Apr 25;12:1527167. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1527167. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40351767 Free PMC article.
-
Gnetin C Intercepts MTA1-Associated Neoplastic Progression in Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 8;14(24):6038. doi: 10.3390/cancers14246038. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551523 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

