Milk and Meat Allergens from Bos taurus β-Lactoglobulin, α-Casein, and Bovine Serum Albumin: An In-Vivo Study of the Immune Response in Mice
- PMID: 31487844
- PMCID: PMC6769769
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11092095
Milk and Meat Allergens from Bos taurus β-Lactoglobulin, α-Casein, and Bovine Serum Albumin: An In-Vivo Study of the Immune Response in Mice
Abstract
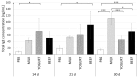
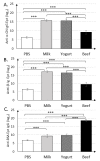
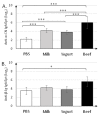
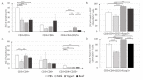
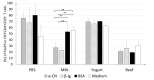
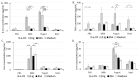
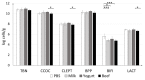
The mechanism of food allergy may vary. This study aimed to compare the effects of milk, yogurt, or beef meat supplementation on humoral and cellular immune responses in a mice model. Mice were divided into four groups: The "Milk group" was sensitized with a β-lactoglobulin (β-lg)/α-casein (α-CN) mixture and supplemented cow milk; the "Yogurt group" was sensitized with β-lg/α-CN and supplemented yogurt; the "Beef group" was immunized with bovine serum albumin (BSA) and supplemented beef meat; and the "PBS group" received PBS in all procedures. ELISA was used to measure humoral response, including: Total IgE, specific IgG, and IgA. Cellular response was determined by phenotyping lymphocyte from lymphoid tissue and measuring the Th1/Th2 cytokine concentration with flow cytometry. The qPCR method was used for quantification of the fecal microbiota. The results obtained revealed a lower IgE level for the Yogurt group than for the Milk one. In the Yogurt group, the contribution of regulatory T cells to MLN and PP was higher compared to the other groups. We confirmed that diet supplementation with yogurt modulates the immune response to the prime allergen, and changes the activity of serum antibodies to milk proteins and BSA. Based on a specific antibodies level, we cannot exclude the possibility of CMA mice reaction against BSA.
Keywords: beef; cow milk; cross-reactivity; immune response; mice allergy model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differences in Regulatory Mechanisms Induced by β-Lactoglobulin and κ-Casein in Cow's Milk Allergy Mouse Model-In Vivo and Ex Vivo Studies.Nutrients. 2021 Jan 25;13(2):349. doi: 10.3390/nu13020349. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33503831 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Low-Immunogenic Yogurt Drinks and Probiotic Bacteria on Immunoreactivity of Cow's Milk Proteins and Tolerance Induction-In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Nutrients. 2020 Nov 4;12(11):3390. doi: 10.3390/nu12113390. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33158132 Free PMC article.
-
Milk Allergen Micro-Array (MAMA) for Refined Detection of Cow's-Milk-Specific IgE Sensitization.Nutrients. 2023 May 21;15(10):2401. doi: 10.3390/nu15102401. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37242284 Free PMC article.
-
Cow's milk allergens identification by two-dimensional immunoblotting and mass spectrometry.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2004 Oct;48(5):363-9. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200400011. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2004. PMID: 15672476
-
Recent perspective on cow's milk allergy and dairy nutrition.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(27):7503-7517. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1915241. Epub 2021 May 13. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022. PMID: 33983082 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Atherosclerotic Properties of Wild Rice in Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor Knockout Mice: The Gut Microbiome, Cytokines, and Metabolomics Study.Nutrients. 2019 Nov 28;11(12):2894. doi: 10.3390/nu11122894. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31795092 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Effect of β-Lactoglobulin Immunization in Mice with Mild Intestinal Deterioration Caused by Low-Dose Dextran Sulphate Sodium: A New Experimental Approach to Allergy Studies.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 10;16(20):3430. doi: 10.3390/nu16203430. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39458426 Free PMC article.
-
OVA-Experienced CD4+ T Cell Transfer and Chicken Protein Challenge Affect the Immune Response to OVA in a Murine Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 18;22(12):6573. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126573. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34207474 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in Regulatory Mechanisms Induced by β-Lactoglobulin and κ-Casein in Cow's Milk Allergy Mouse Model-In Vivo and Ex Vivo Studies.Nutrients. 2021 Jan 25;13(2):349. doi: 10.3390/nu13020349. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33503831 Free PMC article.
-
Study protocol: The role of milk matrix lipids in programming the immunoreactivity of proteins derived from lactic acid bacteria.PLoS One. 2024 May 20;19(5):e0301477. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301477. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38768108 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wróblewska B., Juśkiewicz J., Kroplewski B., Jurgoński A., Wasilewska E., Złotkowska D., Markiewicz L.H. The effect of whey and soy proteins on growth performance, gastroinestinal digestion and selected physiological responses in rats. Food Funct. 2018;9:1500–1509. doi: 10.1039/C7FO01204G. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mierzejewska D., Kubicka E. Effect of temperature on immumorective properties of cow milk whey protein. I. alpha-lactoalbumin. Milchwiss. Milk Sci. Int. 2003;61:237–246.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

