Molecular Characteristics and Treatment of Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with COPD: A Review Article
- PMID: 31487864
- PMCID: PMC6770145
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20184329
Molecular Characteristics and Treatment of Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with COPD: A Review Article
Abstract
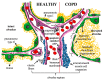
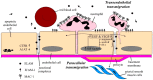
Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) show systemic consequences, such as chronic systemic inflammation leading to changes in the airway, airway penetrability, and endothelial function. Endothelial dysfunction is characterized by a list of alterations of endothelium towards reduced vasodilation, proinflammatory state, detachment and apoptosis of endothelial cells, and development of atherosclerosis. COPD-induced endothelial dysfunction is associated with elevated cardiovascular risk. The increment of physical activities such as pulmonary rehabilitation (PR) training have a significant effect on COPD, thus, PR can be an integrative part of COPD treatment. In this narrative review the focus is on the function of endothelial inflammatory mediators [cytokines, chemokines, and cellular proteases] and pulmonary endothelial cells and endothelial dysfunction in COPD as well as the effects of dysfunction of the endothelium may play in COPD-related pulmonary hypertension. The relationship between smoking and endothelial dysfunction is also discussed. The connection between different pulmonary rehabilitation programs, arterial stiffness and pulse wave velocity (PWV) is presented. Endothelial dysfunction is a significant prognostic factor of COPD, which can be characterized by PWV. We discuss future considerations, like training programs, as an important part of the treatment that has a favorable impact on the endothelial function.
Keywords: COPD; cardiovascular risk; endothelial dysfunction; pulmonary hypertension; pulmonary rehabilitation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Aerobic exercise training does not alter vascular structure and function in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Exp Physiol. 2017 Nov 1;102(11):1548-1560. doi: 10.1113/EP086379. Epub 2017 Sep 30. Exp Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28857336 Clinical Trial.
-
Association Between Systemic and Pulmonary Vascular Dysfunction in COPD.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2020 Aug 26;15:2037-2047. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S257679. eCollection 2020. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2020. PMID: 32904646 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of pulmonary rehabilitation on endothelial function and arterial stiffness in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Physiother Res Int. 2020 Apr;25(2):e1820. doi: 10.1002/pri.1820. Epub 2019 Dec 27. Physiother Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31883231
-
Dysfunction of pulmonary vascular endothelium in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: basic considerations for future drug development.Curr Drug Metab. 2008 Sep;9(7):661-7. doi: 10.2174/138920008785821684. Curr Drug Metab. 2008. PMID: 18781916 Review.
-
Pulmonary vascular involvement in COPD.Chest. 2008 Oct;134(4):808-814. doi: 10.1378/chest.08-0820. Chest. 2008. PMID: 18842913 Review.
Cited by
-
The Combination of Hemogram Indexes to Predict Exacerbation in Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Dec 9;7:572435. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.572435. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33381510 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of vasodilators on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 15;103(46):e39794. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039794. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39560512 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological Insights into Cigarette Smoking-Induced Cardiovascular Disease Risk.Cells. 2022 Oct 11;11(20):3190. doi: 10.3390/cells11203190. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36291057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effectiveness of Supplementation with Key Vitamins, Minerals, Antioxidants and Specific Nutritional Supplements in COPD-A Review.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 14;15(12):2741. doi: 10.3390/nu15122741. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37375645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomic profiling of anaerobic and aerobic energy metabolic pathways in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 Jul;246(14):1586-1596. doi: 10.1177/15353702211008808. Epub 2021 May 6. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021. PMID: 33957804 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

