Investigation on Wear Behavior of Cryogenically Treated Ti-6Al-4V Titanium Alloy under Dry and Wet Conditions
- PMID: 31487877
- PMCID: PMC6766037
- DOI: 10.3390/ma12182850
Investigation on Wear Behavior of Cryogenically Treated Ti-6Al-4V Titanium Alloy under Dry and Wet Conditions
Abstract
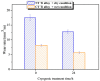
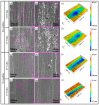
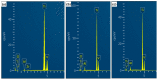
Titanium alloys are widely used in many fields because of their excellent comprehensive properties. However, its poor friction and wear properties limit its many potential applications. In general, the surface roughness of important parts manufactured by titanium alloy should meet certain requirements. As a low-cost and high-efficiency processing method, barrel finishing has been used for the surface finishing of titanium alloys. The main material removal mechanism of barrel finishing is micro-cutting/grinding, which is similar to the material wear mechanism under some conditions. In addition, titanium alloys are subjected to a low force in common surface finishing processes. Cryogenic treatment is a method that can improve the comprehensive properties of titanium alloys. Therefore, the friction and wear behavior of cryogenically treated Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy (CT Ti alloy) and non-cryogenically treated Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy (NT Ti alloy) at a low load and scratch speed was studied comparatively in this paper. The results show that the CT Ti alloy exhibits a lower friction coefficient and wear rate under both dry and wet wear conditions. Under wet conditions, the stabilized friction coefficient is lower than that under dry conditions. The stabilized friction coefficient of CT Ti alloy is 0.18 after reaching a stable wear stage under wet conditions. Under dry wear conditions, the NT Ti alloy mainly showed typical abrasive wear, heavy adhesion wear and oxidation wear characters. The wear mechanisms of CT Ti alloy are mainly abrasive wear, slight adhesion wear and oxidation wear. Under wet wear conditions, the wear mechanism of NT Ti alloy is abrasive wear and slight adhesion wear. After cryogenic treatment, the mechanism for CT Ti alloy is slight abrasive wear.
Keywords: Ti-6Al-4V alloy; cryogenic treatment; wear behavior.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Tribological behavior of Ti-6Al-4V against cortical bone in different biolubricants.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019 Feb;90:460-471. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.10.031. Epub 2018 Oct 29. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019. PMID: 30448560
-
Study on improved tribological properties by alloying copper to CP-Ti and Ti-6Al-4V alloy.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015 Dec 1;57:123-32. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2015.07.046. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015. PMID: 26354247
-
Tribological Properties of Groove-Textured Ti-6Al-4V Alloys with Solid Lubricants in Dry Sliding against GCr15 Steel Balls.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Oct 25;14(11):1978. doi: 10.3390/mi14111978. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004835 Free PMC article.
-
The State of the Art in Machining Additively Manufactured Titanium Alloy Ti-6Al-4V.Materials (Basel). 2023 Mar 24;16(7):2583. doi: 10.3390/ma16072583. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37048881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Shot Peening and Electropolishing Treatment on the Properties of Additively and Conventionally Manufactured Ti6Al4V Alloy: A Review.Materials (Basel). 2024 Feb 17;17(4):934. doi: 10.3390/ma17040934. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399186 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sensor-Assisted Assessment of the Tribological Behavioral Patterns of Al-SiCp Composites under Various Environmental Temperature Conditions.Materials (Basel). 2019 Dec 2;12(23):4004. doi: 10.3390/ma12234004. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31810322 Free PMC article.
-
Material Removal and Surface Integrity Analysis of Ti6Al4V Alloy after Polishing by Flexible Tools with Different Rigidity.Materials (Basel). 2022 Feb 22;15(5):1642. doi: 10.3390/ma15051642. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35268870 Free PMC article.
-
Wear behaviour of titanium based composites reinforced with niobium pentoxide in saline and acidic environments.Heliyon. 2023 Feb 15;9(2):e13737. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13737. eCollection 2023 Feb. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36852048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hollander D.A., von Walter M., Wirtz T., Sellei R., Schmidt-Rohlfing B., Paar O., Erli H.J. Structural, mechanical and in vitro characterization of individually structured Ti-6Al-4V produced by direct laser forming. Biomaterials. 2006;27:955–963. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.07.041. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen C., Feng X.F., Shen Y.F. A comparative investigation on bi-layer Al-Cr/Al-Si coating and mono-layer Al-Cr-Si coating synthesized on Ti-6Al-4V alloy substrate by mechanical alloying method. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017;708:639–651. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.03.082. - DOI
-
- Kikuchi S., Yoshida S., Ueno A. Improvement of fatigue properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy under four-point bending by low temperature nitriding. Int. J. Fatigue. 2019;120:134–140. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2018.11.005. - DOI
-
- Rahmati B., Sarhan A.A.D., Basirun W.J., Abas W.A.B.W. Ceramic tantalum oxide thin film coating to enhance the corrosion and wear characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016;676:369–376. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.03.188. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

