N-Terminal Acetylation and C-Terminal Amidation of Spirulina platensis-Derived Hexapeptide: Anti-Photoaging Activity and Proteomic Analysis
- PMID: 31487895
- PMCID: PMC6780235
- DOI: 10.3390/md17090520
N-Terminal Acetylation and C-Terminal Amidation of Spirulina platensis-Derived Hexapeptide: Anti-Photoaging Activity and Proteomic Analysis
Abstract
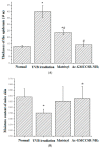
Ultraviolet (UV) irradiation is a potent inducer for skin photoaging. This paper investigated the anti-photoaging effects of the acetylated and amidated hexapeptide (AAH), originally identified from Spirulina platensis, in (Ultraviolet B) UVB-irradiated Human immortalized keratinocytes (Hacats) and mice. The results demonstrated that AAH had much lower toxicity on Hacats than the positive matrixyl (81.52% vs. 5.32%). Moreover, AAH reduced MDA content by 49%; increased SOD, CAT, and GSH-Px activities by 103%, 49%, and 116%, respectively; decreased MMP-1 and MMP-3 expressions by 27% and 29%, respectively, compared to UVB-irradiated mice. Employing isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ)-based proteomics, 60 differential proteins were identified, and major metabolic pathways were determined. Network analysis indicated that these differential proteins were mapped into an interaction network composed of two core sub-networks. Collectively, AAH is protective against UVB-induced skin photoaging and has potential application in skin care cosmetics.
Keywords: acetylation; amidation; hexapeptide; photoaging; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










References
-
- Kong S.Z., Shi X.G., Feng X.X., Li W.J., Liu W.H., Chen Z.W., Xie J.H., Lai X.P., Zhang S.X., Zhang X.J., et al. Inhibitory effect of hydroxysafflor yellow a on mouse skin photoaging induced by ultraviolet irradiation. Rejuvenation Res. 2013;16:404–413. doi: 10.1089/rej.2013.1433. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

