Clinical Significance of SERPINA1 Gene and Its Encoded Alpha1-antitrypsin Protein in NSCLC
- PMID: 31487965
- PMCID: PMC6770941
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11091306
Clinical Significance of SERPINA1 Gene and Its Encoded Alpha1-antitrypsin Protein in NSCLC
Abstract
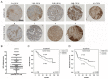
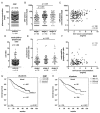
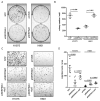
Abstract: High expression of SERPINA1 gene encoding acute phase protein, alpha1-antitrypsin (AAT), is associated with various tumors. We sought to examine the significance of SERPINA1 and AAT protein in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients and NSCLC cell lines. Tumor and adjacent non-tumor lung tissues and serum samples from 351 NSCLC patients were analyzed for SERPINA1 expression and AAT protein levels. We also studied the impact of SERPINA1 expression and AAT protein on H1975 and H661 cell behavior, in vitro. Lower SERPINA1 expression in tumor but higher in adjacent non-tumor lung tissues (n = 351, p = 0.016) as well as higher serum levels of AAT protein (n = 170, p = 0.033) were associated with worse survival rates. Specifically, in NSCLC stage III patients, higher blood AAT levels (>2.66 mg/mL) correlated with a poor survival (p = 0.002). Intriguingly, levels of serum AAT do not correlate with levels of C-reactive protein, neutrophils-to-leukocyte ratio, and do not correlate with SERPINA1 expression or AAT staining in the tumor tissue. Additional experiments in vitro revealed that external AAT and/or overexpressed SERPINA1 gene significantly improve cancer cell migration, colony formation and resistance to apoptosis. SERPINA1 gene and AAT protein play an active role in the pathogenesis of lung cancer and not just reflect inflammatory reaction related to cancer development.
Keywords: SERPINA1; acute phase proteins; alpha1-antitrypsin; apoptosis; inflammation; lung cancer; migration.
Conflict of interest statement
Michael Meister and Sabina Janciauskiene report grants from German Center for Lung Research during the conduct of the study. Thomas Muley reports grants and personal fees from the German Center for Lung Research (DZL) during the conduct of the study and grants and personal fees from Roche outside the submitted work. Marc A Schneider reports grants and personal fees from German Center for Lung Research (DZL) during the conduct of the study. Tobias Welte received travel support and personal fees from Grifols and CSL Behring. Other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Goldstraw P., Chansky K., Crowley J., Rami-Porta R., Asamura H., Eberhardt W.E., Nicholson A.G., Groome P., Mitchell A., Bolejack V., et al. The iaslc lung cancer staging project: Proposals for revision of the tnm stage groupings in the forthcoming (eighth) edition of the tnm classification for lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016;11:39–51. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2015.09.009. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

