Morphological characteristics of ocular toxoplasmosis and its regression pattern on swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography: a case report
- PMID: 31488090
- PMCID: PMC6729000
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-019-1209-8
Morphological characteristics of ocular toxoplasmosis and its regression pattern on swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography: a case report
Abstract
Background: To report the successful treatment of ocular toxoplasmosis and present the use of multimodal imaging to describe the changes in ocular toxoplasmic lesions subsequent to treatment.
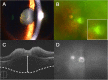
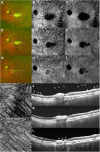
Case presentation: A 73-year-old female visited the clinic with decreased visual acuity in the left eye. Fundus examination showed severe vitreous haze with yellow-white infiltrates near the foveal center. Spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) revealed disorganization of the retinal structure with markedly thickened choroid beneath the active lesion. Highly elevated serum titers of IgG antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii were observed. Topical and systemic steroids with oral Bactrim were administered after a diagnosis of ocular toxoplasmosis was made. After improvement in the severity of vitritis, structural en face swept-source optical coherence tomography (SS-OCT) imaging demonstrated diffuse choroidal dilation with many collateral vascular branches surrounding the active lesion. Eight intravitreal injections of clindamycin (1 mg/0.1 ml) were administered at 1- to 2-week intervals along with systemic antibiotics and steroids. After the treatment, the toxoplasmic lesion resolved to an atrophic chorioretinal scar. Dilated choroidal vessel size was normalized and collateral vascular branches were markedly constricted on structural en face SS-OCT images.
Conclusions: This is the first detailed report on the morphological changes in the choroidal vasculature surrounding ocular toxoplasmic lesions that were characterized using SS-OCT-A imaging. Multimodal imaging with SS-OCT-A can be valuable in clinical diagnosis as well as in clarifying the mechanism of choroidal structural changes in ocular toxoplasmosis.
Keywords: Case report; Morphological changes; Ocular toxoplasmosis; Swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

