Does idiopathic congenital talipes equinovarus have an impact on attainment of developmental milestones? A multicentre international study
- PMID: 31489040
- PMCID: PMC6701447
- DOI: 10.1302/1863-2548.13.190060
Does idiopathic congenital talipes equinovarus have an impact on attainment of developmental milestones? A multicentre international study
Abstract
Purpose: The Ponseti method is a well-established approach to treating clubfoot. Potentially, both the underlying pathology and adherence to post-correction bracing can affect lower limb function and age of independent standing and walking. This cohort study investigates the age at which infants with idiopathic clubfoot treated using the Ponseti method achieved three selected developmental milestones and whether or not this correlated with treatment compliance.
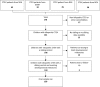
Methods: A prospectively collected database from four centres was visited. Inclusion criteria were patients with idiopathic clubfoot with no comorbidities or prior treatment. Age at attainment of independent standing, walking, nocturnal continence was compared across three groups: I) congenital talipes equinovarus (CTEV) children compliant with treatment; II) CTEV children non-compliant with treatment; and III) typically-developed siblings. Minimum follow-up was five years.
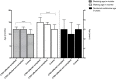
Results: In all, 130 patients (198 feet) fitted the inclusion criteria: 43:87 (F:M). Standing was achieved by a mean 12.0 months in group I (sd 2.50); 12.0 months (sd 2.0) in II and ten months (sd 3.0) in III. Walking was achieved by a mean 15 months (sd 4.0) in group I, 14 months (sd 1.75) in II and 12 months (sd 3) in III, respectively. Both the compliant and non-compliant CTEV children were significantly slower at achieving standing and walking compared to sibling controls (p < 0.0001). There was no significant difference between age of nocturnal continence between the three groups.
Conclusion: Infants with idiopathic clubfoot treated according to the Ponseti method achieve independent standing and walking approximately two months later than their typically-developed siblings. The delay is not related to the use of the foot abduction brace.
Level of evidence: III.
Keywords: Clubfoot; Ponseti; developmental milestones.
Figures


References
-
- Morcuende JA, Dolan LA, Dietz FR, Ponseti IV. Radical reduction in the rate of extensive corrective surgery for clubfoot using the Ponseti method. Pediatrics 2004;113:376-380. - PubMed
-
- Dobbs MB, Rudzki JR, Purcell DB, et al. Factors predictive of outcome after use of the Ponseti method for the treatment of idiopathic clubfeet. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 2004;86-A:22-27. - PubMed
-
- Paulsen-Miller M, Dolan LA, Stineman A, Morcuende JA. Understanding the educational needs for parents of children with clubfoot. Orthop Nurs 2011;30:273-278. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

