International consensus statement on robotic pancreatic surgery
- PMID: 31489304
- PMCID: PMC6700012
- DOI: 10.21037/hbsn.2019.07.08
International consensus statement on robotic pancreatic surgery
Abstract
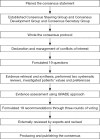
The robotic surgical system has been applied to various types of pancreatic surgery. However, controversies exist regarding a variety of factors including the safety, feasibility, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness of robotic surgery. This study aimed to evaluate the current status of robotic pancreatic surgery and put forth experts' consensus and recommendations to promote its development. Based on the WHO Handbook for Guideline Development, a Consensus Steering Group* and a Consensus Development Group were established to determine the topics, prepare evidence-based documents, and generate recommendations. The GRADE Grid method and Delphi vote were used to formulate the recommendations. A total of 19 topics were analyzed. The first 16 recommendations were generated by GRADE using an evidence-based method (EBM) and focused on the safety, feasibility, indication, techniques, certification of the robotic surgeon, and cost-effectiveness of robotic pancreatic surgery. The remaining three recommendations were based on literature review and expert panel opinion due to insufficient EBM results. Since the current amount of evidence was low/meager as evaluated by the GRADE method, further randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are needed in the future to validate these recommendations.
Keywords: Robotic surgery; consensus statement; pancreatectomy; pancreatic enucleation; pancreaticoduodenectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Comment in
-
Is robotic pancreatic surgery finally ready for prime-time?Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2020 Oct;9(5):650-653. doi: 10.21037/hbsn.2019.12.05. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2020. PMID: 33163516 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Robotic pancreatic surgery: a slowly developing field.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2020 Oct;9(5):673-675. doi: 10.21037/hbsn.2020.02.02. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2020. PMID: 33163522 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical