Risk factors for the recurrence of diabetic foot ulcers among diabetic patients: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 31489774
- PMCID: PMC7949075
- DOI: 10.1111/iwj.13200
Risk factors for the recurrence of diabetic foot ulcers among diabetic patients: a meta-analysis
Erratum in
-
Corrigenda.Int Wound J. 2020 Apr;17(2):523. doi: 10.1111/iwj.13327. Int Wound J. 2020. PMID: 32115897 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
This study aimed to systematically review and identify the risk factors for the recurrence of diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) among diabetic patients. PUBMED, EMBASE, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, China Biology Medicine (CBM), China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), WanFang, and VIP databases were electronically searched to identify eligible studies updated to January 2019 to collect case-control studies or cohort studies on the risk factors for the recurrence of DFUs. Two reviewers independently screened the literature, extracted data, and assessed the risk of bias of included studies using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. A meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.3. Nine retrospective cohort studies were included, in which 1426 patients were enrolled, 542 in the DFU recurrence group and 884 in the non-recurrent DFU group. Risk factors for the recurrence of DFUs included male gender (odds ratio [OR] = 1.38, 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.07-1.78, P < .05), smoking (OR = 1.66, 95% CI, 1.26-2.20, P = .0004), duration of diabetes (WMD = 4.43, 95% CI, 1.96‐6.90, P = .0004), duration of past DFUs (OR = 1.02, 95% CI, 1.00-1.03, P = .006), plantar ulcers (OR = 5.31, 95% CI, 4.93-5.72, P <.00001), peripheral artery disease (OR = 1.65, 95% CI, 1.20-2.28, P = .002), and diabetic peripheral neuropathy (OR = 2.15, 95% CI, 1.40-3.30, P = .0005). No significant differences were found in age, body mass index, total cholesterol, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy, or hypertension. Health care staff should pay attention to the identified risk factors for the recurrence of DFUs. Because of the limited quality and quantity of the included studies, rigorous studies with adequate sample sizes are needed to verify the conclusion.
Keywords: diabetic foot ulcer; meta-analysis; recurrence; risk factor.
© 2019 Medicalhelplines.com Inc and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

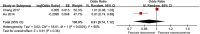


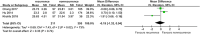
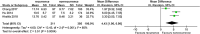
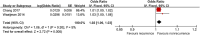





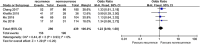
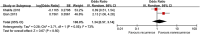
References
-
- Ogurtsova K, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Huang Y, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;128:40‐50. - PubMed
-
- Del Pino‐Sedeno T, Trujillo‐Martin MM, Andia I, et al. Platelet‐rich plasma for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers: a meta‐analysis. Wound Repair Regen. 2018;27(2):170‐182. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong DG, Boulton AJM, Bus SA. Diabetic foot ulcers and their recurrence. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(24):2367‐2375. - PubMed
-
- Khalifa WA. Risk factors for diabetic foot ulcer recurrence: a prospective 2‐year follow‐up study in Egypt. Foot (Edinb). 2018;35:11‐15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

