Maternal Exposure to Bisphenol A Combined with High-Fat Diet-Induced Programmed Hypertension in Adult Male Rat Offspring: Effects of Resveratrol
- PMID: 31489946
- PMCID: PMC6770559
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20184382
Maternal Exposure to Bisphenol A Combined with High-Fat Diet-Induced Programmed Hypertension in Adult Male Rat Offspring: Effects of Resveratrol
Abstract
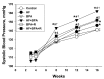
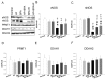
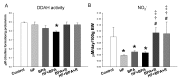
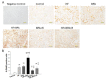
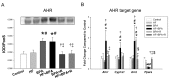
Maternal exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and a high-fat intake may induce the developmental programming of hypertension in adult offspring. Bisphenol A (BPA) is one of the most commonly environmental EDCs. As the nitric oxide (NO) and aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) signaling pathways both contribute to the pathogenesis of hypertension, we evaluated whether resveratrol, an antioxidant and an AHR antagonist, can prevent hypertension programmed by a maternal BPA and HF diet. Sixteen-week-old male rat offspring were assigned to six groups (n = 8 per group): Control, HF (D12331, Research Diets), BPA (50 μg/kg/day), HF + BPA, BPA + R (resveratrol 50mg/L in drinking water throughout pregnancy and lactation), and HF + BPA + R. Maternal BPA exposure exacerbated hypertension programmed by HF consumption in adult male offspring, which was protected by maternal resveratrol therapy. The BPA and HF diet synergistically induced oxidative stress in offspring kidneys, which resveratrol treatment prevented. We observed that HF + BPA-induced programmed hypertension was associated with a decreased NO bioavailability, increased oxidative stress, and an activated AHR signaling pathway. The beneficial effects of resveratrol are relevant to restoring NO bioavailability, reducing oxidative stress, and antagonizing the AHR signaling pathway. Our results cast a new light on resveratrol as a reprogramming strategy to protect against hypertension programmed by combined BPA and HF exposure, but this strategy has yet to be translated into clinical applications.
Keywords: aryl hydrocarbon receptor; asymmetric dimethylarginine; bisphenol A; developmental origins of health and disease (DOHaD); high-fat diet; hypertension; nitric oxide; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maternal Resveratrol Therapy Protects Male Rat Offspring against Programmed Hypertension Induced by TCDD and Dexamethasone Exposures: Is It Relevant to Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor?Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 20;19(8):2459. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082459. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30127255 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol prevents combined prenatal NG-nitro-L-arginine-methyl ester (L-NAME) treatment plus postnatal high-fat diet induced programmed hypertension in adult rat offspring: interplay between nutrient-sensing signals, oxidative stress and gut microbiota.J Nutr Biochem. 2019 Aug;70:28-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.04.002. Epub 2019 Apr 24. J Nutr Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31108332
-
Protection of Male Rat Offspring against Hypertension Programmed by Prenatal Dexamethasone Administration and Postnatal High-Fat Diet with the Nrf2 Activator Dimethyl Fumarate during Pregnancy.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 14;20(16):3957. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163957. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31416234 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal High-Fat Diet and Offspring Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 25;23(15):8179. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158179. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal Fructose Intake Affects Transcriptome Changes and Programmed Hypertension in Offspring in Later Life.Nutrients. 2016 Nov 25;8(12):757. doi: 10.3390/nu8120757. Nutrients. 2016. PMID: 27897982 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Melatonin Use during Pregnancy and Lactation Complicated by Oxidative Stress: Focus on Offspring's Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Health in Animal Models.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Feb 12;13(2):226. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020226. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gestational exposure to high fat diets and bisphenol A alters metabolic outcomes in dams and offspring, but produces hepatic steatosis only in dams.Chemosphere. 2022 Jan;286(Pt 2):131645. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131645. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 34426127 Free PMC article.
-
Preventive Aspects of Early Resveratrol Supplementation in Cardiovascular and Kidney Disease of Developmental Origins.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 19;22(8):4210. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084210. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33921641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal Models for Studying Developmental Origins of Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome.Biomedicines. 2025 Feb 12;13(2):452. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020452. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40002865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breastfeeding and Future Cardiovascular, Kidney, and Metabolic Health-A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2025 Mar 12;17(6):995. doi: 10.3390/nu17060995. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40290039 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

