Design, methodology, and preliminary results of the follow-up of a population-based cohort study in rural area of northern China: Handan Eye Study
- PMID: 31490265
- PMCID: PMC6797155
- DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000418
Design, methodology, and preliminary results of the follow-up of a population-based cohort study in rural area of northern China: Handan Eye Study
Abstract
Background: Handan Eye Study (HES), a large population-based cohort study in rural area of northern China, was one of the few studies focusing on the major eye diseases of rural Chinese population. The aim of this study was to introduce the design, methodology and to assess the data quality of the follow-up phase of HES.
Methods: All participants were recruited in Yongnian county of Handan city between 2012 and 2013. Main outcomes were measured by visual quality scales and ocular examinations. We performed the Chi-square test to make comparison of categorical data among groups, One-way analysis of variance and Kruskal-Wallis test was applied to make comparison of continuous data among groups, a post-hoc test was done to make further pairwise comparison. Inter-class correlation coefficients (ICCs) and Kappa coefficients were used to evaluate the consistency between different operators. Logistic regression was used to explore the influence factors of death, odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were used to estimate the effect size of each influence factor.
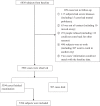
Results: The follow-up rate was 85.3%. Subjects were classified into three groups: the follow-up group (n = 5394), the loss to follow-up group (n = 929), and the dead group (n = 507), comparison of their baseline information was done. Compared with the other two groups, age of the dead group (66.52 ± 10.31 years) was the oldest (Z = 651.293, P < 0.001), male proportion was the highest (59.0%) (χ = 42.351, P < 0.001), only 65.9% of the dead finished middle school education (Z = 205.354, P < 0.001). The marriage percentage, body mass index (BMI), best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), and intra-ocular pressure of the dead group was the lowest either. Spherical equivalent error (SER) of the dead group was the highest. Besides, history of smoking, hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease were more common in the dead group. Multivariate analysis showed that age (OR = 1.901, 95% CI: 1.074-1.108), gender (OR = 0.317, 95% CI: 0.224-0.448), and BCVA (OR = 0.282, 95% CI: 0.158-0.503) were associated with death. While between the follow-up group and the loss to follow-up group, there was only difference on age, gender, BMI, systolic blood pressure and SER. The Cronbach coefficients of all scales used in the follow-up were ≥0.63 and the cumulative variances were ≥0.61, indicating good reliability and validity. The ICCs and Kappa coefficients between different operators were ≥0.69.
Conclusions: HES has a high follow-up rate and a low risk of loss to follow-up bias. Age, gender, and BCVA are influence factors of death. Specifically, male subjects are at a higher risk of death than female, age is a risk factor of death while BCVA is a protective factor for death.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rationale, design, methodology, and baseline data of a population-based study in rural China: the Handan Eye Study.Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2009 Mar-Apr;16(2):115-27. doi: 10.1080/09286580902738159. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2009. PMID: 19353400
-
Ocular Trauma in a Rural Population of North China: The Handan Eye Study.Biomed Environ Sci. 2015 Jul;28(7):495-501. doi: 10.3967/bes2015.071. Biomed Environ Sci. 2015. PMID: 26248733
-
Diabetic Retinopathy, Visual Impairment, and the Risk of Six-Year Death: A Cohort Study of a Rural Population in China.Ophthalmic Res. 2021;64(6):983-990. doi: 10.1159/000512667. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Ophthalmic Res. 2021. PMID: 33120387
-
[Changes of eye care use among rural adults under the reform of New Rural Cooperative Medical Scheme: the Handan Eye Study].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Aug 11;54(8):570-579. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0412-4081.2018.08.003. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30107649 Chinese.
-
[Prevalence and risk factors of common blinding ocular diseases among people aged 30 years and above in rural area of Handan].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Dec 29;100(48):3841-3845. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20200824-02452. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33371628 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Five-year incidence of primary glaucoma and related risk factors - The Handan eye study.Acta Ophthalmol. 2023 Feb;101(1):e50-e60. doi: 10.1111/aos.15216. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Acta Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 35822411 Free PMC article.
-
Retinal nerve fibre layer thickness measured with SD-OCT in a population-based study: the Handan Eye Study.Br J Ophthalmol. 2023 Aug;107(8):1156-1164. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2021-320618. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Br J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 35383049 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative analysis of dynamic iris changes in primary angle-closure disease with long axial lengths: the Handan Eye Study.Eye (Lond). 2024 May;38(7):1362-1367. doi: 10.1038/s41433-023-02905-1. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Eye (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38287112 Free PMC article.
-
Macular thickness and its associated factors in a Chinese rural adult population: the Handan Eye Study.Br J Ophthalmol. 2023 Nov 22;107(12):1864-1872. doi: 10.1136/bjo-2022-321766. Br J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36162970 Free PMC article.
-
Progression of Primary Angle Closure Suspect to Primary Angle Closure and Associated Risk Factors: The Handan Eye Study.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Jun 1;62(7):2. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.7.2. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34061952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jie R, Xu L, Wang YX, Zhang L, You QS, Yang H, et al. Ten-year incidence of retinal nerve fiber layer defects: the beijing eye study 2001/2011. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2015; 56:5118–5124. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-16682. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Huang W, He M, Zheng Y, Huang S, Liu B, et al. Causes and five-year incidence of blindness and visual impairment in urban Southern China: the Liwan eye study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2013; 54:4117–4121. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-11911. - PubMed
-
- Ye H, Zhang Q, Liu X, Cai X, Yu W, Yu S, et al. Prevalence of age-related macular degeneration in an elderly urban Chinese population in China: the Jiangning eye study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2014; 55:6374–6380. doi: 10.1167/iovs.14-14899. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Li SZ, Li L, He MG, Thomas R, Wang NL, et al. Dynamic iris changes as a risk factor in primary angle closure disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2016; 57:218–226. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-17651. - PubMed