Calculation of Second Virial Coefficients of Atomistic Proteins Using Fast Fourier Transform
- PMID: 31490691
- PMCID: PMC7032052
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.9b06808
Calculation of Second Virial Coefficients of Atomistic Proteins Using Fast Fourier Transform
Abstract
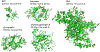
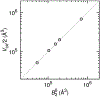
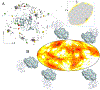
The second virial coefficient, B2, measures a protein solution's deviation from ideal behavior. It is widely used to predict or explain solubility, crystallization condition, aggregation propensity, and critical temperature for liquid-liquid phase separation. B2 is determined by the interaction energy between two protein molecules and, specifically, by the integration of the Mayer f-function in the relative configurational space (translation and rotation) of the two molecules. Simple theoretical models, such as one attributed to Derjaguin, Landau, Verwey, and Overbeek (DLVO), can fit the dependence of B2 on salt concentrations. However, model parameters derived often are physically unrealistic and hardly transferable from protein to protein. Previous B2 calculations incorporating atomistic details were done with limited sampling in the configurational space, due to enormous computational cost. Our FMAP method, based on fast Fourier transform, can considerably accelerate such calculations, and here we adapt it to calculate B2 values for proteins represented at the atomic level in implicit solvent. After tuning of a single parameter in the energy function, FMAPB2 predicts well the B2 values for lysozyme and other proteins over wide ranges of solvent conditions (salt concentration, pH, and temperature). The method is available as a web server at http://pipe.rcc.fsu.edu/fmapb2 .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
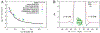
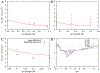
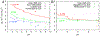


References
-
- Rosenbaum DF; Zukoski CF, Protein interactions and crystallization. J Cryst Growth 1996, 169, 752–758.
-
- George A; Wilson WW, Predicting protein crystallization from a dilute solution property. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 1994, 50, 361–365. - PubMed
-
- Vliegenthart GA; Lekkerkerker HNW, Predicting the gas-liquid critical point from the second virial coefficient. J Chem Phys 2000, 112, 5364–5369.
-
- Hill TL, An Introduction to Statistical Thermodynamics. Dover Publications, Inc.: New York, 1986.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

