Renal denervation improves sodium excretion in rats with chronic heart failure: effects on expression of renal ENaC and AQP2
- PMID: 31490733
- PMCID: PMC6879918
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00299.2019
Renal denervation improves sodium excretion in rats with chronic heart failure: effects on expression of renal ENaC and AQP2
Abstract
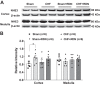
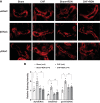
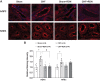
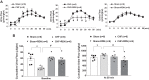
Previously we have shown that increased expression of renal epithelial sodium channels (ENaC) may contribute to the renal sodium and water retention observed during chronic heart failure (CHF). The goal of this study was to examine whether renal denervation (RDN) changed the expressions of renal sodium transporters ENaC, sodium-hydrogen exchanger-3 proteins (NHE3), and water channel aquaporin 2 (AQP2) in rats with CHF. CHF was produced by left coronary artery ligation in rats. Four weeks after ligation surgery, surgical bilateral RDN was performed. The expression of ENaC, NHE3, and AQP2 in both renal cortex and medulla were measured. As a functional test for ENaC activation, diuretic and natriuretic responses to ENaC inhibitor benzamil were monitored in four groups of rats (Sham, Sham+RDN, CHF, CHF+RDN). Western blot analysis indicated that RDN (1 wk later) significantly reduced protein levels of α-ENaC, β-ENaC, γ-ENaC, and AQP2 in the renal cortex of CHF rats. RDN had no significant effects on the protein expression of kidney NHE3 in both Sham and CHF rats. Immunofluorescence studies of kidney sections confirmed the reduced signaling of ENaC and AQP2 in the CHF+RDN rats compared with the CHF rats. There were increases in diuretic and natriuretic responses to ENaC inhibitor benzamil in rats with CHF. RDN reduced the diuretic and natriuretic responses to benzamil in CHF rats. These findings suggest a critical role for renal nerves in the enhanced expression of ENaC and AQP2 and subsequent pathophysiology of renal sodium and water retention associated with CHF.NEW & NOTEWORTHY This is the first study to show in a comprehensive way that renal denervation initiated after a period of chronic heart failure reduces the expression of epithelial sodium channels and aquaporin 2 leading to reduced epithelial sodium channel function and sodium retention.
Keywords: heart failure; renal function; renal nerve; sympathetic nerve activity.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

