Retrospective longitudinal study of ALS in Cyprus: Clinical characteristics, management and survival
- PMID: 31490941
- PMCID: PMC6730913
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220246
Retrospective longitudinal study of ALS in Cyprus: Clinical characteristics, management and survival
Abstract
Introduction: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a rare, progressive neurodegenerative disease. There is heterogeneity of clinical phenotypes while a clinical characterization of ALS in Cyprus is still lacking. The aim of this 30-year retrospective study of ALS in Cyprus is to determine the demographic characteristics of patients, the clinical features of the disease, the uptake of supportive therapies and factors influencing survival.
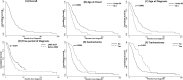
Methods: All ALS patients seen at the Cyprus Institute of Neurology and Genetics from January 1985 until July 2015 were included. Medical records of eligible patients were used for data extraction and compilation of an ALS database. Clinical features were compared between gender categories using univariate tests, while survival was assessed using Kaplan-Meier curves. Cox proportional hazards models were used to identify prognostic factors for survival.
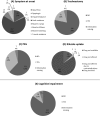
Results: One hundred and seventy-nine ALS patients were included in the study, of whom 7 had a positive family history. Most clinical characteristics of ALS did not differ from what is observed in other European countries. However, some clinical characteristics were unique to our population, such as an increased acceptability and utilisation of supportive treatments such as gastrostomy.
Conclusions: Overall, clinical characteristics of patients with ALS in the Republic of Cyprus do not differ from other European counties. Our study demonstrates a high acceptance and utilisation of supportive interventions enhancing survival, in the context of a multidisciplinary approach offered in the single tertiary centre that services the whole Cypriot ALS population. The findings of this paper are of value to the health professionals treating ALS in Cyprus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

