Single Amino Acid Change Underlies Distinct Roles of H2A.Z Subtypes in Human Syndrome
- PMID: 31491386
- PMCID: PMC7103420
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.08.002
Single Amino Acid Change Underlies Distinct Roles of H2A.Z Subtypes in Human Syndrome
Abstract
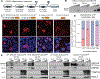
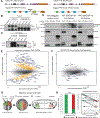
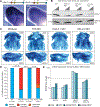
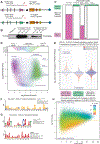
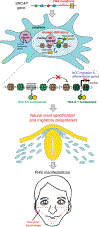
The developmental disorder Floating-Harbor syndrome (FHS) is caused by heterozygous truncating mutations in SRCAP, a gene encoding a chromatin remodeler mediating incorporation of histone variant H2A.Z. Here, we demonstrate that FHS-associated mutations result in loss of SRCAP nuclear localization, alter neural crest gene programs in human in vitro models and Xenopus embryos, and cause craniofacial defects. These defects are mediated by one of two H2A.Z subtypes, H2A.Z.2, whose knockdown mimics and whose overexpression rescues the FHS phenotype. Selective rescue by H2A.Z.2 is conferred by one of the three amino acid differences between the H2A.Z subtypes, S38/T38. We further show that H2A.Z.1 and H2A.Z.2 genomic occupancy patterns are qualitatively similar, but quantitatively distinct, and H2A.Z.2 incorporation at AT-rich enhancers and expression of their associated genes are both sensitized to SRCAP truncations. Altogether, our results illuminate the mechanism underlying a human syndrome and uncover selective functions of H2A.Z subtypes during development.
Keywords: H2A.Z; SRCAP; chromatin remodeler; craniofacial; enhancers; epigenetics; genetic mutation; histone variant; human disorder; neural crest.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
The Face of Chromatin Variants.Cell. 2019 Sep 5;178(6):1284-1286. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.08.024. Cell. 2019. PMID: 31491382
References
-
- Alexa A & Rahnenfuhrer J, 2018. topGO: Enrichment Analysis for Gene Ontology. R package version 2.34.0.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

