Inhibition of Pancreatic α-amylase by Resveratrol Derivatives: Biological Activity and Molecular Modelling Evidence for Cooperativity between Viniferin Enantiomers
- PMID: 31491840
- PMCID: PMC6766848
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24183225
Inhibition of Pancreatic α-amylase by Resveratrol Derivatives: Biological Activity and Molecular Modelling Evidence for Cooperativity between Viniferin Enantiomers
Abstract
To improve the current understanding of the role of stilbenoids in the management of diabetes, the inhibition of the pancreatic α-amylase by resveratrol derivatives was investigated. To approach in a systematic way, the mechanistic and structural aspects of the interaction, potential bioactive agents were prepared as single molecules, that were used for the biological evaluation of the determinants of inhibitory binding. Some dimeric stilbenoids-in particular, viniferin isomers- were found to be better than the reference drug acarbose in inhibiting the pancreatic α-amylase. Racemic mixtures of viniferins were more effective inhibitors than the respective isolated pure enantiomers at an equivalent total concentration, and displayed cooperative effects not observed with the individual enantiomers. The molecular docking analysis provided a thermodynamics-based rationale for the measured inhibitory ability and for the observed synergistic effects. Indeed, the binding of additional ligands on the surface of the alpha-amylase was found to decrease the dissociation constant of inhibitors bound to the active site of the enzyme, thus providing a mechanistic rationale for the observed inhibitory synergies.
Keywords: enzyme inhibition; food bioactives synergism; molecular docking; pancreatic alpha-amylase; resveratrol; stilbenoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
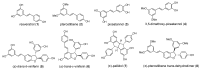







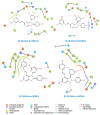
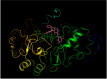
References
-
- Kazeem M.I., Raimi O.G., Balogun R.M., Ogundajo A.L. Comparative study on the α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory potential of different extracts of Blighia sapida Koenig. Am. J. Res. Commun. 2013;1:178–192.

