Erythroid Progenitor Cells in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) May Be Persistently and Productively Infected with Piscine Orthoreovirus (PRV)
- PMID: 31491892
- PMCID: PMC6784031
- DOI: 10.3390/v11090824
Erythroid Progenitor Cells in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) May Be Persistently and Productively Infected with Piscine Orthoreovirus (PRV)
Abstract
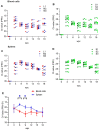
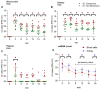
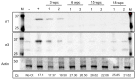
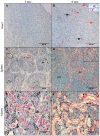
Piscine orthoreovirus (PRV-1) can cause heart and skeletal muscle inflammation (HSMI) in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). The virus targets erythrocytes in the acute peak phase, followed by cardiomyocytes, before the infection subsides into persistence. The persistent phase is characterized by high level of viral RNA, but low level of viral protein. The origin and nature of persistent PRV-1 are not clear. Here, we analyzed for viral persistence and activity in various tissues and cell types in experimentally infected Atlantic salmon. Plasma contained PRV-1 genomic dsRNA throughout an 18-week long infection trial, indicating that viral particles are continuously produced and released. The highest level of PRV-1 RNA in the persistent phase was found in kidney. The level of PRV-1 ssRNA transcripts in kidney was significantly higher than that of blood cells in the persistent phase. In-situ hybridization assays confirmed that PRV-1 RNA was present in erythroid progenitor cells, erythrocytes, macrophages, melano-macrophages and in some additional un-characterized cells in kidney. These results show that PRV-1 establishes a productive, persistent infection in Atlantic salmon and that erythrocyte progenitor cells are PRV target cells.
Keywords: PRV-1; erythroid progenitor cells; persistence; piscine orthoreovirus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
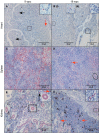
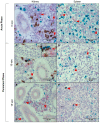
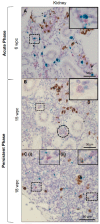
References
-
- Taranger G.L., Karlsen O., Bannister R.J., Glover K.A., Husa V., Karlsbakk E., Kvamme B.O., Boxaspen K.K., Bjorn P.A., Finstad B., et al. Risk assessment of the environmental impact of norwegian atlantic salmon farming. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2015;72:997–1021. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/fsu132. - DOI
-
- Lovoll M., Wiik-Nielsen J., Grove S., Wiik-Nielsen C.R., Kristoffersen A.B., Faller R., Poppe T., Jung J., Pedamallu C.S., Nederbragt A.J., et al. A novel totivirus and piscine reovirus (prv) in atlantic salmon (salmo salar) with cardiomyopathy syndrome (cms) Virol. J. 2010;7:309. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-309. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Palacios G., Lovoll M., Tengs T., Hornig M., Hutchison S., Hui J., Kongtorp R.T., Savji N., Bussetti A.V., Solovyov A., et al. Heart and skeletal muscle inflammation of farmed salmon is associated with infection with a novel reovirus. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e11487. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011487. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wessel O., Braaen S., Alarcon M., Haatveit H., Roos N., Markussen T., Tengs T., Dahle M.K., Rimstad E. Infection with purified piscine orthoreovirus demonstrates a causal relationship with heart and skeletal muscle inflammation in atlantic salmon. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0183781. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183781. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

