Binding of SU(VAR)3-9 Partially Depends on SETDB1 in the Chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 31491894
- PMCID: PMC6769583
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8091030
Binding of SU(VAR)3-9 Partially Depends on SETDB1 in the Chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
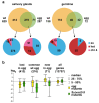
H3K9 methylation is known to play a critical role in gene silencing. This modification is established and maintained by several enzymes, but relationships between them are not fully understood. In the present study, we decipher the interplay between two Drosophila H3K9-specific histone methyltransferases, SU(VAR)3-9 and SETDB1. We asked whether SETDB1 is required for targeting of SU(VAR)3-9. Using DamID-seq, we obtained SU(VAR)3-9 binding profiles for the chromosomes from larval salivary glands and germline cells from adult females, and compared profiles between the wild type and SETDB1-mutant backgrounds. Our analyses indicate that the vast majority of single copy genes in euchromatin are targeted by SU(VAR)3-9 only in the presence of SETDB1, whereas SU(VAR)3-9 binding at repeated sequences in heterochromatin is largely SETDB1-independent. Interestingly, piRNA clusters 42AB and 38C in salivary gland chromosomes bind SU(VAR)3-9 regardless of SETDB1, whereas binding to the same regions in the germline cells is SETDB1-dependent. In addition, we compared SU(VAR)3-9 profiles in female germline cells at different developmental stages (germarium cells in juvenile ovaries and mature nurse cells). It turned out that SU(VAR)3-9 binding is influenced both by the presence of SETDB1, as well as by the differentiation stage.
Keywords: Drosophila; SETDB1; SU(VAR)3-9; chromosome 4; female germline; heterochromatin; piRNA clusters; salivary glands.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors express no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Iyer L.M., Abhiman S., Aravind L. Natural History of Eukaryotic DNA Methylation Systems. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2011;101:25–104. - PubMed
-
- Copur O., Gorchakov A., Finkl K., Kuroda M.I., Muller J. Sex-Specific Phenotypes of Histone H4 Point Mutants Establish Dosage Compensation as the Critical Function of H4k16 Acetylation in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2018;115:13336–13341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1817274115. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

