The Eye as a Window to Systemic Infectious Diseases: Old Enemies, New Imaging
- PMID: 31492008
- PMCID: PMC6780210
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8091392
The Eye as a Window to Systemic Infectious Diseases: Old Enemies, New Imaging
Abstract
Background: Syphilis, tuberculosis and toxoplasmosis are major infectious diseases worldwide; all of them are multisystem pathologies and share a possible ocular involvement. In this context, a fundamental help for the definitive diagnosis is provided by the ophthalmologist, through clinical evaluation and with the aid of a multimodal imaging examination.
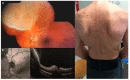
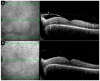
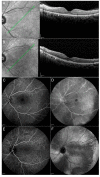
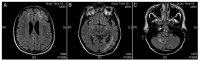
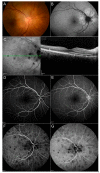
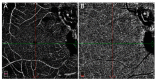
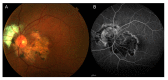
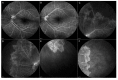
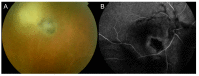
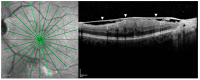
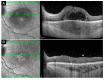
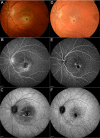
Methods: We hereby describe selected cases who came to our attention and were visited in our eye clinic. In all clinics, the use of retinal and optic disc multimodal imaging during ophthalmological evaluation allowed to make a diagnosis of an infectious disease.
Results: In our tertiary referral center more than 60 patients with syphilis, tuberculosis and toxoplasmosis have been evaluated in the last two years: In 60% of cases the ophthalmological evaluation was secondary to a previous diagnosis of an infectious disease, while in the remaining cases the ophthalmologist, with the help of a multimodal imaging examination and clinical evaluation, represented the physician who leads to the diagnosis.
Conclusion: Our results confirm how in these life-threatening pathologies a prompt diagnosis is mandatory and may benefit from a multidisciplinary and multimodal imaging approach, especially during ophthalmological evaluation.
Keywords: fluorescein angiography; fundus autofluorescence; indocyanine green angiography; infectious uveitis; optical coherence tomography; optical coherence tomography angiography; syphilis; toxoplasmosis; tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance. [(accessed on 5 August 2019)];2017 Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/std/stats17/default.htm.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

