Role of Nutrition and Exercise Programs in Reducing Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 31492032
- PMCID: PMC6780911
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8091393
Role of Nutrition and Exercise Programs in Reducing Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review
Abstract
The combined effect of diet and strength training (ST) on blood pressure (BP) seems to be very important for the treatment of prehypertension and hypertension (HT). Therefore, the aim of this study was to determine whether ST alone or combined with nutrition or supplementation has an impact on the arterial pressure reduction in normotensive and hypertensive populations. A systematic computerized literature search was performed according to the PRISMA guidelines using PubMed, Scopus and Google Scholar; only English language studies published from 1999 until 2018 were included. This systematic search identified the results of 303 individuals from nine studies. The ST program alone had a similar effectiveness as the nutrition program (NP) alone; however, their combination did not result in increased effectiveness in terms of a high BP reduction. The consumption of L-citrulline had a similar effect as ST on lowering BP; on the other hand, caffeine led to an increase in BP during the ST session. Our data suggest that a combination of ST 2-3 times a week at moderate intensity and a NP seems to be equally effective in terms of lowering BP (systolic and diastolic) as ST and NP alone.
Keywords: arterial pressure; caffeine; disease prevention; hypertension; resistance training.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
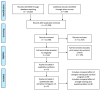
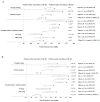
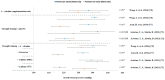
References
-
- Pickering T.G., Hall J.E., Appel L.J., Falkner B.E., Graves J.W., Hill M.N., Jones D.W., Kurtz T., Sheps S.G., Roccella E.J. Recommendations for blood pressure measurement in humans: An AHA scientific statement from the council on high blood pressure research professional and public education subcommittee. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2005;7:102–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2005.04377.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chobanian A.V., Bakris G.L., Black H.R., Cushman W.C., Green L.A., Izzo J.L., Jr., Jones D.W., Materson B.J., Oparil S., Wright J.T., Jr., et al. Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension. 2003;42:1206–1252. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000107251.49515.c2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Meyer K. Resistance exercise in chronic heart failure—Landmark studies and implications for practice. Clin. Investig. Med. 2006;29:166–169. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

