Effect of Baricitinib and Adalimumab in Reducing Pain and Improving Function in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis in Low Disease Activity: Exploratory Analyses from RA-BEAM
- PMID: 31492040
- PMCID: PMC6780319
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8091394
Effect of Baricitinib and Adalimumab in Reducing Pain and Improving Function in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis in Low Disease Activity: Exploratory Analyses from RA-BEAM
Abstract
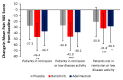
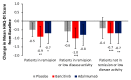
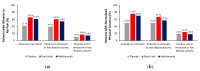
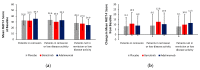
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) may experience residual pain and functional impairment despite good control of disease activity. This study compared improvements in pain and physical function in patients with well-controlled RA after 24 weeks' treatment with baricitinib, adalimumab or placebo in the 52-week RA-BEAM phase III study. Adults with active RA and inadequate response to methotrexate received baricitinib 4 mg once daily, adalimumab 40 mg every two weeks or placebo, with background methotrexate. Patients (N = 1010) were categorised as in remission, in remission or low disease activity, or not in remission or low disease activity at week 24. For patients in remission or low disease activity (n = 310), improvements in mean pain and physical function scores at week 24 were significantly greater with baricitinib than placebo (p < 0.001 and p < 0.01, respectively) and adalimumab (p < 0.05 for both). For both outcomes, differences between adalimumab and placebo were not significant. The proportions of patients in remission or low disease activity with minimal or no pain and with normalised physical function were numerically greater with baricitinib than placebo. Baricitinib 4 mg once daily provided enhanced improvement in pain and physical function in patients with well-controlled RA, suggesting it may produce effects beyond immunomodulation.
Keywords: baricitinib; fatigue; pain; productivity; recovery of function; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
B.F. reports grants from AbbVie, Eli Lilly and Company, MSD, and Pfizer, and personal fees from AbbVie, Biogen, BMS, Celgene, Janssen-Cilag, Eli Lilly and Company, Medac, MSD, NORDIC Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, SOBI and UCB. B.K. reports grants and personal fees from Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, Novartis and UCB. T.T. reports grants and personal fees from Astellas Pharma Inc., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., AbbVie GK, Asahikasei Pharma Corp., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Pfizer Japan Inc., Eisai Co. Ltd., AYUMI Pharmaceutical Corporation, Nipponkayaku Co. Ltd., Novartis Pharma K.K., Bristol–Myers K.K., Astra Zeneca K.K., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Taisho Toyama Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., GlaxoSmithKline K.K., UCB Japan Co. Ltd. and Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. C.G. is an employee and stockholder of Eli Lilly and Company. A.Q. is an employee and stockholder of Eli Lilly and Company. I.d.l.T. is an employee and stockholder of Eli Lilly and Company. B.Z. is an employee and stockholder of Eli Lilly and Company. F.D.L. is an employee and stockholder of Eli Lilly and Company. P.C.T. reports grants from Eli Lilly and Company, and Galapagos, and personal fees from Eli Lilly and Company, AbbVie, Gilead, and Pfizer.
Figures
References
-
- Singh J.A., Saag K.G., Bridges S.L., Jr., Akl E.A., Bannuru R.R., Sullivan M.C., Vaysbrot E., McNaughton C., Osani M., Shmerling R.H., et al. 2015 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68:1–26. doi: 10.1002/art.39480. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Smolen J.S., Landewé R., Bijlsma J., Burmester G., Chatzidionysiou K., Dougados M., Nam J., Ramiro S., Voshaar M., Van Vollenhoven R., et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017;76:960–977. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210715. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nieuwenhuis W.P., De Wit M.P., Boonen A., Van Der Helm-Van Mil A.H. Changes in the clinical presentation of patients with rheumatoid arthritis from the early 1990s to the years 2010: Earlier identification but more severe patient reported outcomes. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016;75:2054–2056. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209949. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ishiguro N., Dougados M., Cai Z., Zhu B., Ishida M., Sato M., Gaich C., Quebe A., Stoykov I., Tanaka Y. Relationship between disease activity and patient-reported outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis: Post hoc analyses of overall and Japanese results from two phase 3 clinical trials. Mod. Rheumatol. 2018;28:950–959. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2017.1422232. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

