Amelioration of Both Central and Peripheral Neuropathy in Mouse Models of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes by the Neurogenic Molecule NSI-189
- PMID: 31492662
- PMCID: PMC6804627
- DOI: 10.2337/db19-0271
Amelioration of Both Central and Peripheral Neuropathy in Mouse Models of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes by the Neurogenic Molecule NSI-189
Abstract
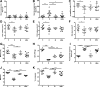
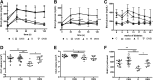
While peripheral neuropathy is the most common complication of long-term diabetes, cognitive deficits associated with encephalopathy and myelopathy also occur. Diabetes is a risk factor for Alzheimer disease (AD) and increases the risk of progression from mild cognitive impairment to AD. The only current recommendation for preventing or slowing the progression of peripheral neuropathy is to maintain close glycemic control, while there is no recommendation for central nervous system disorders. NSI-189 is a new chemical entity that when orally administered promotes neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus, increases hippocampal volume, enhances synaptic plasticity, and reduces cognitive dysfunction. To establish the potential for impact on peripheral neuropathy, we first showed that NSI-189 enhances neurite outgrowth and mitochondrial functions in cultured adult rat primary sensory neurons. Oral delivery of NSI-189 to murine models of type 1 (female) and type 2 (male) diabetes prevented multiple functional and structural indices of small and large fiber peripheral neuropathy, increased hippocampal neurogenesis, synaptic markers and volume, and protected long-term memory. NSI-189 also halted progression of established peripheral and central neuropathy. NSI-189, which is currently in clinical trials for treatment of major depressive disorder, offers the opportunity for the development of a single therapeutic agent against multiple indices of central and peripheral neuropathy.
© 2019 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Enhancement of Mitochondrial Function by the Neurogenic Molecule NSI-189 Accompanies Reversal of Peripheral Neuropathy and Memory Impairment in a Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes.J Diabetes Res. 2022 Jul 4;2022:8566970. doi: 10.1155/2022/8566970. eCollection 2022. J Diabetes Res. 2022. PMID: 35967127 Free PMC article.
-
NSI-189, a small molecule with neurogenic properties, exerts behavioral, and neurostructural benefits in stroke rats.J Cell Physiol. 2017 Oct;232(10):2731-2740. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25847. Epub 2017 Apr 25. J Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28181668 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of synaptic plasticity and reversal of impairments in motor and cognitive functions in a mouse model of Angelman Syndrome by a small neurogenic molecule, NSI-189.Neuropharmacology. 2019 Jan;144:337-344. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.10.038. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30408487
-
The neurogenic compound, NSI-189 phosphate: a novel multi-domain treatment capable of pro-cognitive and antidepressant effects.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017 Jun;26(6):767-770. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2017.1324847. Epub 2017 May 8. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28460574 Review.
-
Peripheral Neuropathy in Mouse Models of Diabetes.Curr Protoc Mouse Biol. 2016 Sep 1;6(3):223-255. doi: 10.1002/cpmo.11. Curr Protoc Mouse Biol. 2016. PMID: 27584552 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of serum magnesium level with small fiber neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Mar 4;12:1509820. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1509820. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40103795 Free PMC article.
-
Using Corneal Confocal Microscopy to Identify Therapeutic Agents for Diabetic Neuropathy.J Clin Med. 2022 Apr 21;11(9):2307. doi: 10.3390/jcm11092307. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35566433 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction following repeated administration of alprazolam causes attenuation of hippocampus-dependent memory consolidation in mice.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Oct 5;15(19):10428-10452. doi: 10.18632/aging.205087. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37801512 Free PMC article.
-
Muscarinic Toxin 7 Signals Via Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase Kinase β to Augment Mitochondrial Function and Prevent Neurodegeneration.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Jun;57(6):2521-2538. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-01900-x. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32198698 Free PMC article.
-
Building Compassion and Human Bridges through Research Collaborations.ACS Omega. 2022 Jan 6;7(2):1542-1546. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c04916. eCollection 2022 Jan 18. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35071851 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bril V. The perfect clinical trial. Int Rev Neurobiol 2016;127:27–41 - PubMed
-
- Pop-Busui R, Martin C. Neuropathy in the DCCT/EDIC-what was done then and what we would do better now. Int Rev Neurobiol 2016;127:9–25 - PubMed
-
- Biessels GJ, Staekenborg S, Brunner E, Brayne C, Scheltens P. Risk of dementia in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol 2006;5:64–74 - PubMed
-
- Riederer P, Korczyn AD, Ali SS, et al. . The diabetic brain and cognition. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 2017;124:1431–1454 - PubMed
-
- Brands AM, Biessels GJ, de Haan EH, Kappelle LJ, Kessels RP. The effects of type 1 diabetes on cognitive performance: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2005;28:726–735 - PubMed

