Long valley lifetime of dark excitons in single-layer WSe2
- PMID: 31492874
- PMCID: PMC6731252
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-12129-1
Long valley lifetime of dark excitons in single-layer WSe2
Abstract
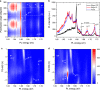
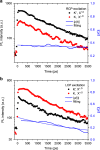
Single-layer transition metal dichalcogenides provide a promising material system to explore the electron's valley degree of freedom as a quantum information carrier. The valley degree of freedom can be directly accessed by means of optical excitation. However, rapid valley relaxation of optically excited electron-hole pairs (excitons) through the exchange interaction has been a major roadblock. Theoretically such valley relaxation is suppressed in dark excitons, suggesting a potential route for long valley lifetimes. Here we develop a waveguide-based method to detect time-resolved and energy-resolved dark exciton emission in single-layer WSe2, which involves spin-forbidden optical transitions with an out-of-plane dipole moment. The valley degree of freedom of dark excitons is accessed through the valley-dependent Zeeman effect under an out-of-plane magnetic field. We find a short valley lifetime for the dark neutral exciton, likely due to the short-range electron-hole exchange, but long valley lifetimes exceeding several nanoseconds for the dark charged excitons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

