Clinical Model for Predicting Warfarin Sensitivity
- PMID: 31492893
- PMCID: PMC6731233
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-49329-0
Clinical Model for Predicting Warfarin Sensitivity
Abstract
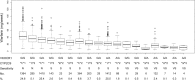
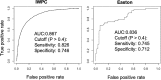
Warfarin is a widely used anticoagulant with a narrow therapeutic index and large interpatient variability in the therapeutic dose. Complications from inappropriate warfarin dosing are one of the most common reasons for emergency room visits. Approximately one third of warfarin dose variability results from common genetic variants. Therefore, it is very necessary to recognize warfarin sensitivity in individuals caused by genetic variants. Based on combined polymorphisms in CYP2C9 and VKORC1, we established a clinical classification for warfarin sensitivity. In the International Warfarin Pharmacogenetic Consortium (IWPC) with 5542 patients, we found that 95.1% of the Black in the IWPC cohort were normal warfarin responders, while 74.8% of the Asian were warfarin sensitive (P < 0.001). Moreover, we created a clinical algorithm to predict warfarin sensitivity in individual patients using logistic regression. Compared to a fixed-dose approach, the clinical algorithm provided significantly better performance. In addition, we validated the derived clinical algorithm using the external Easton cohort with 106 chronic warfarin users. The AUC was 0.836 vs. 0.867 for the Easton cohort and the IWPC cohort, respectively. With the use of this algorithm, it is very likely to facilitate patient care regarding warfarin therapy, thereby improving clinical outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
VKORC1 and CYP2C9 genotypes in Egyptian patients with warfarin resistance.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2016 Mar;27(2):121-6. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0000000000000168. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2016. PMID: 24978953
-
Prediction of sensitivity to warfarin based on VKORC1 and CYP2C9 polymorphisms in patients from different places in Colombia.Biomedica. 2016 Mar 3;36(1):91-100. doi: 10.7705/biomedica.v36i1.2795. Biomedica. 2016. PMID: 27622442
-
Pharmacogenetic-guided and clinical warfarin dosing algorithm assessments with bleeding outcomes risk-stratified by genetic and covariate subgroups.Int J Cardiol. 2020 Oct 15;317:159-166. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.03.055. Epub 2020 Mar 21. Int J Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32505370
-
Clinical Practice Recommendations on Genetic Testing of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 Variants in Warfarin Therapy.Ther Drug Monit. 2015 Aug;37(4):428-36. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000000192. Ther Drug Monit. 2015. PMID: 26186657 Review.
-
Extremely low therapeutic doses of acenocoumarol in a patient with CYP2C9*3/*3 and VKORC1-1639A/A genotype.Pharmacogenomics. 2019 Apr;20(5):311-317. doi: 10.2217/pgs-2018-0189. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Pharmacogenomics. 2019. PMID: 30983536 Review.
Cited by
-
Ensemble of machine learning algorithms using the stacked generalization approach to estimate the warfarin dose.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 19;13(10):e0205872. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205872. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30339708 Free PMC article.
-
Warfarin sensitivity is associated with increased hospital mortality in critically Ill patients.PLoS One. 2022 May 5;17(5):e0267966. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267966. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35511891 Free PMC article.
-
Personalized medicine in cardiovascular disease: review of literature.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2021 Jul 7;20(2):1793-1805. doi: 10.1007/s40200-021-00840-0. eCollection 2021 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2021. PMID: 34900826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of warfarin population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics model in Han population based on Bayesian method.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 27;14(1):14846. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65048-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38937509 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical