Whole-genome sequencing-based epidemiological analysis of anti-tuberculosis drug resistance genes in Japan in 2007: Application of the Genome Research for Asian Tuberculosis (GReAT) database
- PMID: 31492902
- PMCID: PMC6731343
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-49219-5
Whole-genome sequencing-based epidemiological analysis of anti-tuberculosis drug resistance genes in Japan in 2007: Application of the Genome Research for Asian Tuberculosis (GReAT) database
Abstract
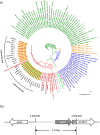
We investigated the lineages of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) isolates from the RYOKEN study in Japan in 2007 and the usefulness of genotypic drug susceptibility testing (DST) using the Genome Research for Asian Tuberculosis (GReAT) database. In total, 667 isolates were classified into lineage 1 (4.6%), lineage 2 (0.8%), lineage 2/Beijing (72.1%), lineage 3 (0.5%), and lineage 4 (22.0%). The nationality, gender, and age groups associated with the isolates assigned to lineage 1 were significantly different from those associated with other lineages. In particular, isolates of lineage 1.2.1 (EAI2) formed sub-clusters and included a 2,316-bp deletion in the genome. The proportion of the isolates resistant to at least one anti-tuberculosis (TB) drug was 10.8%, as determined by either the genotypic or phenotypic method of DST. However, the sensitivities to isoniazid, streptomycin, and ethambutol determined by the genotypic method were low. Thus, unidentified mutations in the genome responsible for drug resistance were explored, revealing previously unreported mutations in the katG, gid, and embB genes. This is the first nationwide report of whole-genome analysis of TB in Japan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Reechaipichitkul, W., Tubtim, S. & Chaimanee, P. Drug susceptibility patterns of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and clinical outcomes of drug-resistant tuberculosis at Srinagarind Hospital, a tertiary care center in northeastern Thailand. The Southeast Asian journal of tropical medicine and public health. 42(5), 1154–62 (2011 Sep). - PubMed
-
- Elmi Omar Sald, Hasan Habsah, Abdullah Sarimah, Mat Jeab Mat Zuki, Bin Alwi Zilfalil, Naing Nyi Nyi. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis and risk factors associated with its development: a retrospective study. The Journal of Infection in Developing Countries. 2015;9(10):1076–1085. doi: 10.3855/jidc.6162. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

