Prospective Study of a Novel, Radiation-Free, Reduced-Intensity Bone Marrow Transplantation Platform for Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases
- PMID: 31493539
- PMCID: PMC6942248
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2019.08.018
Prospective Study of a Novel, Radiation-Free, Reduced-Intensity Bone Marrow Transplantation Platform for Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases
Abstract
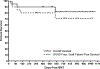
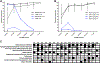
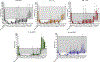
Allogeneic blood or marrow transplantation (BMT) is a potentially curative therapy for patients with primary immunodeficiency (PID). Safe and effective reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) approaches that are associated with low toxicity, use alternative donors, and afford good immune reconstitution are needed to advance the field. Twenty PID patients, ranging in age from 4 to 58 years, were treated on a prospective clinical trial of a novel, radiation-free and serotherapy-free RIC, T-cell-replete BMT approach using pentostatin, low-dose cyclophosphamide, and busulfan for conditioning with post-transplantation cyclophosphamide-based graft-versus-host-disease (GVHD) prophylaxis. This was a high-risk cohort with a median hematopoietic cell transplantation comorbidity index of 3. With median follow-up of survivors of 1.9 years, 1-year overall survival was 90% and grade III to IV acute GVHD-free, graft-failure-free survival was 80% at day +180. Graft failure incidence was 10%. Split chimerism was frequently observed at early post-BMT timepoints, with a lower percentage of donor T cells, which gradually increased by day +60. The cumulative incidences of grade II to IV and grade III to IV acute GVHD (aGVHD) were 15% and 5%, respectively. All aGVHD was steroid responsive. No patients developed chronic GVHD. Few significant organ toxicities were observed. Evidence of phenotype reversal was observed for all engrafted patients, even those with significantly mixed chimerism (n = 2) or with unknown underlying genetic defect (n = 3). All 6 patients with pre-BMT malignancies or lymphoproliferative disorders remain in remission. Most patients have discontinued immunoglobulin replacement. All survivors are off immunosuppression for GVHD prophylaxis or treatment. This novel RIC BMT approach for patients with PID has yielded promising results, even for high-risk patients.
Keywords: Bone marrow transplantation; Post-transplantation cyclophosphamide; Primary immunodeficiency; Reduced-intensity conditioning.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phase II Trial of Graft-versus-Host Disease Prophylaxis with Post-Transplantation Cyclophosphamide after Reduced-Intensity Busulfan/Fludarabine Conditioning for Hematological Malignancies.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015 May;21(5):906-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2015.01.026. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015. PMID: 25667989 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Reduced Intensity Bone Marrow Transplantation with Post-Transplant Cyclophosphamide for Pediatric Inherited Immune Deficiencies and Bone Marrow Failure Syndromes.J Clin Immunol. 2021 Feb;41(2):414-426. doi: 10.1007/s10875-020-00898-0. Epub 2020 Nov 6. J Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33159275 Free PMC article.
-
Unmanipulated haploidentical bone marrow transplantation and posttransplantation cyclophosphamide for hematologic malignancies after myeloablative conditioning.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013 Jan;19(1):117-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2012.08.014. Epub 2012 Aug 29. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013. PMID: 22940057 Clinical Trial.
-
Alloreactivity as therapeutic principle in the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Studies of clinical and immunologic aspects of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with nonmyeloablative conditioning.Dan Med Bull. 2007 May;54(2):112-39. Dan Med Bull. 2007. PMID: 17521527 Review.
-
Treatment-related mortality and graft-versus-leukemia activity after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for chronic lymphocytic leukemia using intensity-reduced conditioning.Leukemia. 2003 May;17(5):841-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2402905. Leukemia. 2003. PMID: 12750695 Review.
Cited by
-
Innovative Cell-Based Therapies and Conditioning to Cure RAG Deficiency.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 19;11:607926. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.607926. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33329604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of Relapsing HPV Diseases by Restored Function of Natural Killer Cells.N Engl J Med. 2021 Sep 2;385(10):921-929. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2102715. N Engl J Med. 2021. PMID: 34469647 Free PMC article.
-
Intermediate-dose posttransplantation cyclophosphamide for myeloablative HLA-haploidentical bone marrow transplantation.Blood Adv. 2025 May 27;9(10):2553-2569. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024014879. Blood Adv. 2025. PMID: 39908565 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Separating the Wheat From the Chaff in Asthma and Bronchiectasis: The Saga Trajectory of a Patient With Adult-Onset RAG1 Deficiency.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2023 Jun;11(6):1972-1980. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2023.04.005. Epub 2023 Apr 23. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2023. PMID: 37088379 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Beyond fludarabine: pentostatin plus cyclophosphamide are a well-tolerated alternative in reduced intensity conditioning.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2022 Dec;57(12):1837-1838. doi: 10.1038/s41409-022-01819-y. Epub 2022 Sep 17. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2022. PMID: 36115868 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Rosenberg E, Dent PB, Denburg JA. Primary Immune Deficiencies in the Adult: A Previously Underrecognized Common Condition. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2016;4:1101–7. - PubMed
-
- Connelly JA. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant for a New Primary Immunodeficiency Disorder: A Voyage Where No Transplant Physician Has Gone Before. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2017;23:863–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

