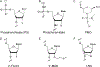Manipulation of renal gene expression using oligonucleotides
- PMID: 31493813
- PMCID: PMC7992197
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.mcb.2019.05.006
Manipulation of renal gene expression using oligonucleotides
Abstract
Oligonucleotides are small molecules 8-50 nucleotides in length that bind via Watson-Crick base pairing to enhance or repress the expression of target RNA. The use of oligonucleotides to manipulate gene expression in the kidney could be a valuable tool to further understand kidney pathophysiology and can serve as an important complement to genetic studies. This chapter serves as a primer on the use of oligonucleotides in the kidney. We provide an overview of the various ways that oligonucleotides can manipulate gene expression. In addition, we describe the advancements in the development of oligonucleotides for laboratory and clinical use. Finally, instruction is provided on the design and implementation of oligonucleotides for in vitro and in vivo laboratory studies.
Keywords: Antisense oligonucleotides; Gene expression; MicroRNA; Oligonucleotides; RNA; Therapeutics.
© 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The remaining authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antisense-mediated angiotensinogen inhibition slows polycystic kidney disease in mice with a targeted mutation in Pkd2.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015 Feb 15;308(4):F349-57. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00478.2014. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25537744 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA-binding protein bicaudal C regulates polycystin 2 in the kidney by antagonizing miR-17 activity.Development. 2010 Apr;137(7):1107-16. doi: 10.1242/dev.046045. Development. 2010. PMID: 20215348 Free PMC article.
-
Polycystin-1 binds Par3/aPKC and controls convergent extension during renal tubular morphogenesis.Nat Commun. 2013;4:2658. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3658. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 24153433 Free PMC article.
-
Polycystic kidney disease in 2011: Connecting the dots toward a polycystic kidney disease therapy.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011 Dec 13;8(2):66-8. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2011.196. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 22158473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs as targets for antisense-based therapeutics.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2008 Jan;8(1):59-81. doi: 10.1517/14712598.8.1.59. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18081537 Review.
Cited by
-
Renal Ciliopathies: Sorting Out Therapeutic Approaches for Nephronophthisis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 13;9:653138. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.653138. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34055783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs: Midfielders of Cardiac Health, Disease and Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 11;24(22):16207. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216207. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review on the bioanalysis of non-virus-based gene therapeutics.Bioanalysis. 2024 Dec-Dec;16(23-24):1279-1294. doi: 10.1080/17576180.2024.2437418. Epub 2024 Dec 14. Bioanalysis. 2024. PMID: 39673530 Review.
-
The role of PPARα in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2020 Jul;29(4):432-438. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000615. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2020. PMID: 32427692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oligonucleotide therapies for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Mar 30;35(2):102184. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102184. eCollection 2024 Jun 11. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 38665220 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altmann KH, Fabbro D, Dean NM, Geiger T, Monia BP, Muller M, et al. (1996). Second-generation antisense oligonucleotides: Structure-activity relationships and the design of improved signal-transduction inhibitors. Biochemical Society Transactions, 24(3), 630–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical