Intracellular cardiomyocytes potential recording by planar electrode array and fibroblasts co-culturing on multi-modal CMOS chip
- PMID: 31494510
- PMCID: PMC8559116
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2019.111626
Intracellular cardiomyocytes potential recording by planar electrode array and fibroblasts co-culturing on multi-modal CMOS chip
Abstract
Intracellular action potential signals reveal enriched physiological information. Patch clamp techniques have been widely used to measure intracellular potential. Despite their high signal fidelity, they suffer from low throughput. Recently, 3D nanoelectrodes have been developed for intracellular potential recording. However, they are limited by scalability, yield, and cost, directly constraining their use in monitoring large number of cells and high throughput applications. In this paper, we demonstrate intracellular potential monitoring of cardiomyocytes using simple 2D planar electrode array in a standard CMOS process without patch clamps or post fabricated 3D nanoelectrodes. This is enabled by our unique cardiomyocytes/fibroblasts co-culturing technique and electroporation. The co-cultured fibroblasts promote tight sealing of cardiomyocytes on electrodes and enable high-fidelity intracellular potential monitoring based on 2D planar electrode. Compared to existing technologies, our platform has a unique potential to achieve an unprecedented combination of throughput, spatiotemporal resolution, and a tissue-level field-of-view for cellular electrophysiology monitoring.
Keywords: CMOS; Cardiomyocytes; Cellular impedance sensing; Drug screening; Intracellular action potential recording; Multimodality sensor array.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

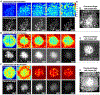
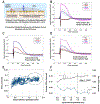
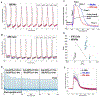

References
-
- Abbott J, Ye T, Qin L, Jorgolli M, Gertner R, Ham D, and Park H, 2017. CMOS nanoelectrode array for all-electrical intracellular electrophysiological imaging. Nat. Nanotechnol 12, 460–466. - PubMed
-
- Aiba T, Shimizu W, Inagaki M, Noda T, Miyoshi S, Ding W, Zankov D, Toyoda F, Matsuura H, Horie M, and Sunagawa K, 2005. Cellular and ionic mechanism for drug-induced long QT syndrome and effectiveness of verapamil. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 45, 300–307. - PubMed
-
- Baumann R, Brischwein M, Schwinde A, Stegbauer K, and Wolf B, 1997. Monitoring of cellular behaviour by impedance measurements on interdigitated electrode structures Biosensor and Bioelectronics 12, 29–41. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

