Sequential Factorized Autoencoder for Localizing the Origin of Ventricular Activation From 12-Lead Electrocardiograms
- PMID: 31494539
- PMCID: PMC7051887
- DOI: 10.1109/TBME.2019.2939138
Sequential Factorized Autoencoder for Localizing the Origin of Ventricular Activation From 12-Lead Electrocardiograms
Abstract
Objective: This work presents a novel approach to handle the inter-subject variations existing in the population analysis of ECG, applied for localizing the origin of ventricular tachycardia (VT) from 12-lead electrocardiograms (ECGs).
Methods: The presented method involves a factor disentangling sequential autoencoder (f-SAE) - realized in both long short-term memory (LSTM) and gated recurrent unit (GRU) networks - to learn to disentangle the inter-subject variations from the factor relating to the location of origin of VT. To perform such disentanglement, a pair-wise contrastive loss is introduced.
Results: The presented methods are evaluated on ECG dataset with 1012 distinct pacing sites collected from scar-related VT patients during routine pace-mapping procedures. Experiments demonstrate that, for classifying the origin of VT into the predefined segments, the presented f-SAE improves the classification accuracy by 8.94% from using prescribed QRS features, by 1.5% from the supervised deep CNN network, and 5.15% from the standard SAE without factor disentanglement. Similarly, when predicting the coordinates of the VT origin, the presented f-SAE improves the performance by 2.25 mm from using prescribed QRS features, by 1.18 mm from the supervised deep CNN network and 1.6 mm from the standard SAE.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate the importance as well as the feasibility of the presented f-SAE approach for separating inter-subject variations when using 12-lead ECG to localize the origin of VT.
Significance: This work suggests the important research direction to deal with the well-known challenge posed by inter-subject variations during population analysis from ECG signals.
Figures




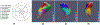


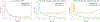



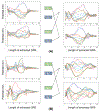
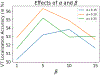
References
-
- PARK KYOUNG-MIN, KIM YOU-HO, and Marchlinski Francis E, “Using the surface electrocardiogram to localize the origin of idiopathic ventricular tachycardia,” Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, vol. 35, no. 12, pp. 1516–1527, 2012. - PubMed
-
- Miller JOHNM, Marchlinski FRANCISE, Buxton Alfred E, and Josephson Mark E, “Relationship between the 12-lead electrocardiogram during ventricular tachycardia and endocardial site of origin in patients with coronary artery disease.,” Circulation, vol. 77, no. 4, pp. 759–766, 1988. - PubMed
-
- Sapp John L, Bar-Tal Meir, Howes Adam J, Toma Jonathan E, El-Damaty Ahmed, Warren James W, MacInnis Paul J, Zhou Shijie, and Horáček B Milan, “Real-time localization of ventricular tachycardia origin from the 12-lead electrocardiogram,” JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology, vol. 3, no. 7, pp. 687–699, 2017. - PubMed
-
- Potse Mark, Linnenbank André C, Peeters Heidi AP, Sippens-Groenewegen Arne, and Crimbergen CA, “Continuous localization of cardiac activation sites using a database of multichannel ecg recordings,” IEEE transactions on biomedical engineering, vol. 47, no. 5, pp. 682–689, 2000. - PubMed

