Systemic biomarkers of inflammation, oxidative stress and tissue injury and repair among waterpipe, cigarette and dual tobacco smokers
- PMID: 31494573
- PMCID: PMC7050420
- DOI: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2019-054958
Systemic biomarkers of inflammation, oxidative stress and tissue injury and repair among waterpipe, cigarette and dual tobacco smokers
Abstract
Background: Waterpipe tobacco (WPT) smoking is associated with deleterious effects on cardio-pulmonary systems which may have adverse repercussions in pathophysiology and progression of chronic lung and cardiovascular diseases. We compared the biomarkers of systemic inflammation, lipid mediators, injury/repair and oxidative stress between groups of non-smokers (NS), exclusive WPT smokers (WPS), exclusive cigarette smokers (CS) and dual WPS and CS (DS).
Methods: Two cohorts were recruited. Cohort I consisted of WPS (n=12), CS (n=26), DS (n=10) and NS (n=25). Cohort II consisted of WPS (n=33) and NS (n=24). Plasma and urine samples were collected and analysed for various systemic biomarkers.
Results: Compared with NS, plasma levels of inflammatory mediators (interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, IL1β and tumor necrosis factor-α) were significantly higher in WPS and CS, and were further augmented in DS. Endothelial biomarkers (intracellular adhesion molecule-1, prostaglandin E-2 and metalloproteinase-9) were significantly higher in CS. Most notably, pro-resolving lipid mediator (resolvin E1) and biomarkers of immunity, tissue injury, and repair were significantly lower in WPS and CS. Urinary levels of 8-isoprostane were significantly higher in all smoking groups in cohort I, while 8-isoprostane, myeloperoxidase, receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE), En-RAGE and matrix metalloproteinase-9 were significantly higher in all smoking groups in cohort II.
Conclusions: Biomarkers of inflammation, oxidative stress, immunity, tissue injury and repair were elevated in WPS and CS groups. Furthermore, concurrent use of WPT and cigarettes is more harmful than cigarette or WPT smoking alone. These data may help inform the public and policy-makers about the dangers of WPT smoking and dual use of tobacco products.
Keywords: biomarkers; cigarette smokers; hookah; inflammation; oxidative stress; waterpipe.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


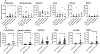
References
-
- Waziry R, Jawad M, Ballout RA, et al. The effects of waterpipe tobacco smoking on health outcomes: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Epidemiol 2017;46:32–43. - PubMed
-
- Warnakulasuriya S Waterpipe smoking, oral cancer and other oral health effects. Evid Based Dent 2011;12:44–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
