Comparison of rapid BACpro® II, Sepsityper® kit and in-house preparation methods for direct identification of bacteria from blood cultures by MALDI-TOF MS with and without Sepsityper® module analysis
- PMID: 31494828
- PMCID: PMC6800852
- DOI: 10.1007/s10096-019-03654-4
Comparison of rapid BACpro® II, Sepsityper® kit and in-house preparation methods for direct identification of bacteria from blood cultures by MALDI-TOF MS with and without Sepsityper® module analysis
Abstract
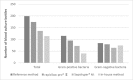
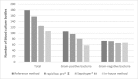
There are several approaches available for purifying microorganisms prior to matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) analysis. In the present study, rapid BACpro® II (Nittobo Medical Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), a new application, has been compared with Sepsityper® kit (Bruker Daltonics, Billerica, USA) and an in-house method. Samples were also tested with two modules, standard and Sepsityper®, identified in the Bruker MALDI-TOF MS. The bottles having monomicrobial growth were included in the study according to Gram staining results. In total, two hundred blood culture bottles were included but there was no growth in one of the subcultures so 199 blood culture bottles were studied prospectively. With the standard MALDI-TOF MS analysis, rapid BACpro® II could successfully identify microorganisms in 174/199 (87.4%) of the bottles where Sepsityper® kit and in-house method were successful in 136/199 (68.3%) and 114/199 (57.3%), respectively. When the MALDI-TOF MS data were analysed by Sepsityper® module, the identification rates were increased to 94.4%, 82.1% and 69.8% (p < 0.001), respectively. In the Sepsityper® module, 72/73 (98.6%) of Gram-negative and 97/106 (91.5%) of Gram-positive microorganisms were detected by rapid BACpro® II method. The present study shows that rapid BACpro® II is a reliable preparation procedure and has higher rates of identification compared with Sepsityper® kit and in-house method. The use of the Sepsityper® module in blood cultures increases the chance of identification for all three methods studied.
Keywords: Blood culture; MALDI-TOF MS; Rapid BACpro II; Sepsityper® kit; Sepsityper® module.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Paolucci M, Landini MP, Sambri V. Conventional and molecular techniques for the early diagnosis of bacteraemia. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2010;36(Suppl 2):S6–S16. - PubMed
-
- Peralta G, Roiz MP, Sánchez MB, Garrido JC, Ceballos B, Rodríguez-Lera MJ, Mateos F, De Benito I. Time-to-positivity in patients with Escherichia coli bacteraemia. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2007;13:1077–1082. - PubMed
-
- Cattoir L, Coorevits L, Leroux-Roels I, Claeys G, Verhasselt B, Boelens J. Improving timelines in reporting results from positive blood cultures: simulation of impact of rapid identification on therapy on a real-life cohort. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018;37(12):2253–2260. - PubMed
-
- Seifert H. The clinical importance of microbiological findings in the diagnosis and management of bloodstream infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48(Suppl 4):S238–S245. - PubMed
-
- Peters RP, van Agtmael MA, Danner SA, Savelkoul PH. Vandenbroucke-Grauls CM (2004) New developments in the diagnosis of bloodstream infections. Lancet Infect Dis. 2004;4(12):751–760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

