Comparative Analyses of Pharmaceuticals or Food Supplements Containing Chondroitin Sulfate: Are Their Bioactivities Equivalent?
- PMID: 31494830
- PMCID: PMC6822805
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-019-01064-8
Comparative Analyses of Pharmaceuticals or Food Supplements Containing Chondroitin Sulfate: Are Their Bioactivities Equivalent?
Abstract
Introduction: Oral supplementation of chondroitin sulfate (CS) and glucosamine (GlcN), symptomatic slow-acting molecules, is recommended by European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases (ESCEO) and other European Union (EU) guidelines for the restoration of the articular cartilage surface in patients affected by osteoarthritis (OA). They are commercialized as pharmaceutical grade products and as food supplements in combination with plant extracts hyaluronic acid, methylsulfonylmethane, and other components. Food supplements do not need to undergo the strict regulatory controls of pharmaceutical grade products; thus, composition and contaminants that could be present may not be evidenced before commercialization and these uncertainties may give rise to concerns about the bioactivity of these formulations.
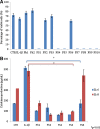
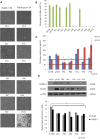
Methods: In this paper 10 different food supplements (FS) from diverse European countries were analyzed in comparison with two pharmaceutical grade products (Ph) using updated analytical approaches and biochemical cell-based assays. The purity, the titer, and the origin of CS in Ph and FS samples were initially assessed in order to successively compare the biological function. Both food supplements and pharmaceutical formulations were tested in vitro, using the same final CS concentration, on primary chondrocytes and synoviocytes in terms of (i) cell viability, (ii) activation of the NF-κB-mediated inflammation pathway, (iii) cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP-2), IL-6, and IL-8 production.
Results: All the FS presented a certain insoluble fraction; the CS and the GlcN contents were lower than the declared ones in 9/10 and 8/10 samples, respectively. All FS contained keratan sulfate (KS) at up to 50% of the total glycosaminoglycan amount declared on the label. Primary cells treated with the samples diluted to present the same CS concentration in the medium showed cytotoxicity in 7/10 FS while Ph preserved viability and reduced NF-κB, COMP-2, and secreted inflammatory cytokines.
Conclusion: Among all samples tested, the pharmaceutical grade products demonstrated effective modulation of biomarkers counteracting the inflammation status and improving viability and the physiological condition of OA human primary chondrocyte and synoviocyte cells. In contrast to that, most FS were cytotoxic at the tested concentrations, and only 3/10 of them showed similarities to Ph sample behavior in vitro.
Funding: This work was partially supported by PON01_1226 NUTRAFAST, MIUR Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca Scientifica. Bioteknet financed two short-term grants for graduate technicians. The journal's Rapid Service and Open Access fees were funded by IBSA CH.
Keywords: Chondroitin sulfate; Food supplements; Glucosamine; HPAE-PAD; Human primary chondrocytes; Human primary synoviocytes; Keratan sulfate; NF-κB mediated inflammation pathway; OA in vitro model; Rheumatology.
Figures



References
-
- Chevalier X, Conrozier T. Access to highly purified chondroitin sulfate for appropriate treatment of osteoarthritis: a review. MA@PoC. 2017;1(1):134–144.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

