Piezo1 mechanosensitive channels: what are they and why are they important
- PMID: 31494839
- PMCID: PMC6815293
- DOI: 10.1007/s12551-019-00584-5
Piezo1 mechanosensitive channels: what are they and why are they important
Abstract
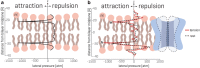
Mechanosensitive (MS) ion channels are integral membrane proteins which play a crucial role in fast signaling during mechanosensory transduction processes in living cells. They are ubiquitous and old in the evolutionary sense, given their presence in cells from all three kingdoms of life found on Earth, including bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryotic organisms. As molecular transducers of mechanical force, MS channels are activated by mechanical stimuli exerted on cellular membranes, upon which they rapidly and efficiently convert these stimuli into electrical, osmotic, and/or chemical intracellular signals. Most of what we know about the gating mechanisms of MS channels comes from the work carried out on bacterial channels. However, recent progress resulting from identification and structural information of eukaryotic K2P-type TREK and TRAAK as well as Piezo1 and Piezo2 MS channels has greatly contributed to our understanding of the common biophysical principles underlying the gating mechanism and evolutionary origins of these fascinating membrane proteins. Using Piezo1 channels as an example, we briefly describe in this review what we have learned about their biophysics, physiological functions, and potential roles in "mechanopathologies."
Keywords: Force-from-filament; Force-from-lipids; Lipid bilayer; Liposome reconstitution; Patch clamp; Transbilayer pressure profile.
Figures

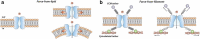

References
-
- Albuisson J, Murthy SE, Bandell M, Coste B, Louis-Dit-Picard H, Mathur J, Feneant-Thibault M, Tertian G, De Jaureguiberry JP, Syfuss PY, Cahalan S, Garcon L, Toutain F, Simon Rohrlich P, Delaunay J, Picard V, Jeunemaitre X, Patapoutian A. Dehydrated hereditary stomatocytosis linked to gain-of-function mutations in mechanically activated PIEZO1 ion channels. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1884. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bass RB, Strop P, Barclay M, Rees DC. Crystal structure of Escherichia coli MscS, a voltage-modulated and mechanosensitive channel. Science. 2002;298:1582–1587. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

