Synaptic vesicle fusion is modulated through feedback inhibition by dopamine auto-receptors
- PMID: 31494966
- PMCID: PMC7336876
- DOI: 10.1002/syn.22131
Synaptic vesicle fusion is modulated through feedback inhibition by dopamine auto-receptors
Abstract
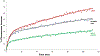
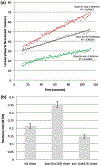
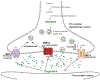
Mechanisms of synaptic vesicular fusion and neurotransmitter clearance are highly controlled processes whose finely-tuned regulation is critical for neural function. This modulation has been suggested to involve pre-synaptic auto-receptors; however, their underlying mechanisms of action remain unclear. Previous studies with the well-defined C. elegans nervous system have used functional imaging to implicate acid sensing ion channels (ASIC-1) to describe synaptic vesicle fusion dynamics within its eight dopaminergic neurons. Implementing a similar imaging approach with a pH-sensitive fluorescent reporter and fluorescence resonance after photobleaching (FRAP), we analyzed dynamic imaging data collected from individual synaptic termini in live animals. We present evidence that constitutive fusion of neurotransmitter vesicles on dopaminergic synaptic termini is modulated through DOP-2 auto-receptors via a negative feedback loop. Integrating our previous results showing the role of ASIC-1 in a positive feedback loop, we also put forth an updated model for synaptic vesicle fusion in which, along with DAT-1 and ASIC-1, the dopamine auto-receptor DOP-2 lies at a modulatory hub at dopaminergic synapses. Our findings are of potential broader significance as similar mechanisms are likely to be used by auto-receptors for other small molecule neurotransmitters across species.
Keywords: C. elegans; FRAP; auto-receptor; dopamine; neurotransmitter; synaptic modulation.
© 2019 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Bermingham DP, Hardaway JA, Snarrenberg CL, Robinson SB, Folkes OM, Salimando GJ, … Blakely RD (2016). Acute blockade of the Caenorhabditis elegans dopamine transporter DAT-1 by the mammalian norepinephrine transporter inhibitor nisoxetine reveals the influence of genetic modifications of dopamine signaling in vivo. Neurochemistry International, 98, 122–128. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
