The ubiquitin ligase adaptor SPOP in cancer
- PMID: 31495053
- PMCID: PMC6803047
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.15056
The ubiquitin ligase adaptor SPOP in cancer
Abstract
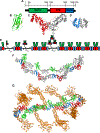
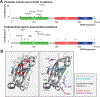
The dysregulation of ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation has emerged as an important mechanism of pathogenesis in several cancers. The speckle-type POZ protein (SPOP) functions as a substrate adaptor for the cullin3-RING ubiquitin ligase and controls the cellular persistence of a diverse array of protein substrates in hormone signalling, epigenetic control and cell cycle regulation, to name a few. Mutations in SPOP and the resulting dysregulation of this proteostatic pathway play causative roles in the pathogenesis of prostate and endometrial cancers, whereas overexpression and mislocalization are associated with kidney cancer. Understanding the molecular mechanism of the normal function of SPOP as well as the cause of SPOP-mediated oncogenesis is thus critical for eventual therapeutic targeting of SPOP and other related pathways. Here, we will review SPOP structure, function and the molecular mechanism of how this function is achieved. We will then review how mutations and protein mislocalization contribute to cancer pathogenesis and will provide a perspective on how SPOP may be targeted therapeutically.
Keywords: SPOP; endometrial cancer; intrinsically disordered proteins; liquid-liquid phase separation; prostate cancer; ubiquitin ligase; ubiquitination.
© 2019 Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Nagai Y, Kojima T, Muro Y, Hachiya T, Nishizawa Y, Wakabayashi T & Hagiwara M (1997) Identification of a novel nuclear speckle-type protein, SPOP, FEBS Lett. 418, 23–6. - PubMed
-
- Kwon JE, La M, Oh KH, Oh YM, Kim GR, Seol JH, Baek SH, Chiba T, Tanaka K, Bang OS, Joe CO & Chung CH (2006) BTB domain-containing speckle-type POZ protein (SPOP) serves as an adaptor of Daxx for ubiquitination by Cul3-based ubiquitin ligase, J Biol Chem. 281, 12664–72. - PubMed
-
- Hernandez-Munoz I, Lund AH, van der Stoop P, Boutsma E, Muijrers I, Verhoeven E, Nusinow DA, Panning B, Marahrens Y & van Lohuizen M (2005) Stable X chromosome inactivation involves the PRC1 Polycomb complex and requires histone MACROH2A1 and the CULLIN3/SPOP ubiquitin E3 ligase, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 102, 7635–40. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kent D, Bush EW & Hooper JE (2006) Roadkill attenuates Hedgehog responses through degradation of Cubitus interruptus, Development. 133, 2001–10. - PubMed
-
- Zhuang M, Calabrese MF, Liu J, Waddell MB, Nourse A, Hammel M, Miller DJ, Walden H, Duda DM, Seyedin SN, Hoggard T, Harper JW, White KP & Schulman BA (2009) Structures of SPOP-substrate complexes: insights into molecular architectures of BTB-Cul3 ubiquitin ligases, Mol Cell. 36, 39–50. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

