Effect of lutein on methotrexate-induced oxidative lung damage in rats: a biochemical and histopathological assessment
- PMID: 31495083
- PMCID: PMC6823580
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2018.145
Effect of lutein on methotrexate-induced oxidative lung damage in rats: a biochemical and histopathological assessment
Abstract
Background/aims: This study aimed to investigate the effect of lutein on methotrexate (MTX)-induced pulmonary toxicity in rats biochemically and histopathologically.
Methods: The rats in the MTX + lutein (MTXL, n = 6) group were given 1 mg/kg of lutein orally. A 0.9% NaCl solution was administered orally to the MTX (n = 6) group and the healthy group (HG, n = 6). One hour later, a single 20 mg/kg dose of MTX was injected intraperitoneally in the MTXL and MTX. Lutein or 0.9% NaCl solution was administered once a day for 5 days. At the end of this period, malondialdehyde (MDA), myeloperoxidase (MPO), total glutathione (tGSH), interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β), and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) were measured in the lung tissues from the animals euthanized with 50 mg/kg thiopental sodium anesthesia. Subsequently, histopathological examinations were performed.
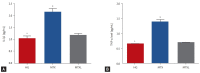
Results: The levels of MDA, MPO, IL-1β, and TNF-α in the lung tissue of the MTX were significantly higher than those of the MTXL and HG groups (p < 0.0001), and the amount of tGSH was lower. The histopathological findings in the MTX group, in which the oxidants and cytokines were higher, were more severe.
Conclusion: Lutein prevented the MTX-induced oxidative lung damage biochemically and histopathologically. This result indicates that lutein may be useful in the treatment of MTX-induced lung damage.
Keywords: Lung; Lutein; Methotrexate; Rats.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protective Effects of Alpha-Lipoic Acid on Methotrexate-Induced Oxidative Lung Injury in Rats.J Invest Surg. 2018 Apr;31(2):107-113. doi: 10.1080/08941939.2017.1296513. Epub 2017 Mar 24. J Invest Surg. 2018. PMID: 28340320
-
Effect of taxifolin on methotrexate-induced oxidative and inflammatory oral mucositis in rats: biochemical and histopathological evaluation.J Appl Oral Sci. 2022 Sep 19;30:e20220115. doi: 10.1590/1678-7757-2022-0115. eCollection 2022. J Appl Oral Sci. 2022. PMID: 36134855 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Resveratrol on Oxidative Stress Induced by Methotrexate in Rat Ileum Tissue: Evaluation of Biochemical and Histopathological Features and Analysis of Gene Expression.Med Princ Pract. 2016;25(2):181-6. doi: 10.1159/000442020. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Med Princ Pract. 2016. PMID: 26517535 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of alpha lipoic acid on rat kidneys in methotrexate induced oxidative injury.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19(11):2132-9. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26125279
-
The effects of lycopene on intestinal injury due to methotrexate in rats.Redox Rep. 2016 May;21(3):113-8. doi: 10.1179/1351000215Y.0000000041. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Redox Rep. 2016. PMID: 26359686 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cinnamic acid mitigates methotrexate-induced lung fibrosis in rats: comparative study with pirfenidone.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Feb;397(2):1071-1079. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02652-w. Epub 2023 Aug 15. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37581637 Free PMC article.
-
The Possible effect of Bosentan on the methotrexate-induced salivary gland changes in male rats: histological and Immunohistochemical study.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2025 Jan 17;14(1):tfaf007. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfaf007. eCollection 2025 Feb. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2025. PMID: 39830884
-
The Protective Effects of Nutraceutical Components in Methotrexate-Induced Toxicity Models-An Overview.Microorganisms. 2022 Oct 18;10(10):2053. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10102053. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36296329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dihydromyricetin Modulates Nrf2 and NF-κB Crosstalk to Alleviate Methotrexate-Induced Lung Toxicity.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Mar 23;16(4):481. doi: 10.3390/ph16040481. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37111238 Free PMC article.
-
Lutein Production and Extraction from Microalgae: Recent Insights and Bioactive Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 1;25(5):2892. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052892. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474137 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moisa A, Fritz P, Benz D, Wehner HD. Iatrogenically-related, fatal methotrexate intoxication: a series of four cases. Forensic Sci Int. 2006;156:154–157. - PubMed
-
- Abolmaali SS, Tamaddon AM, Dinarvand R. A review of therapeutic challenges and achievements of methotrexate delivery systems for treatment of cancer and rheumatoid arthritis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013;71:1115–1130. - PubMed
-
- Ohosone Y, Okano Y, Kameda H, et al. Toxicity of low-dose methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis: clinical characteristics in patients with MTX-induced pancytopenia and interstitial pneumonitis. Ryumachi. 1997;37:16–23. - PubMed
-
- Altindag O, Kucukoglu B. Intoxication due to high dose methotrexate in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis: a case report. Arch Rheumatol. 2011;26:58–60.
-
- Brunton LL, Chabner BA, Knollmann B. Goodman & Gilman’s the Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. 12th ed. New York (NY): McGraw Hill Professional; 2011.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
