Proteomics of Melanoma Response to Immunotherapy Reveals Mitochondrial Dependence
- PMID: 31495571
- PMCID: PMC7993352
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.08.012
Proteomics of Melanoma Response to Immunotherapy Reveals Mitochondrial Dependence
Abstract
Immunotherapy has revolutionized cancer treatment, yet most patients do not respond. Here, we investigated mechanisms of response by profiling the proteome of clinical samples from advanced stage melanoma patients undergoing either tumor infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL)-based or anti- programmed death 1 (PD1) immunotherapy. Using high-resolution mass spectrometry, we quantified over 10,300 proteins in total and ∼4,500 proteins across most samples in each dataset. Statistical analyses revealed higher oxidative phosphorylation and lipid metabolism in responders than in non-responders in both treatments. To elucidate the effects of the metabolic state on the immune response, we examined melanoma cells upon metabolic perturbations or CRISPR-Cas9 knockouts. These experiments indicated lipid metabolism as a regulatory mechanism that increases melanoma immunogenicity by elevating antigen presentation, thereby increasing sensitivity to T cell mediated killing both in vitro and in vivo. Altogether, our proteomic analyses revealed association between the melanoma metabolic state and the response to immunotherapy, which can be the basis for future improvement of therapeutic response.
Keywords: anti-PD-1; cancer metabolism; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immunotherapy; lipid metabolism; mass spectrometry; melanoma; mitochondrial metabolism; proteomics; tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
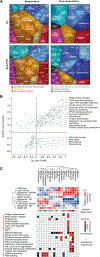


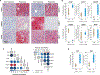


Comment in
-
Helping tumour antigens to the surface.Nat Rev Cancer. 2019 Nov;19(11):608. doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0212-y. Nat Rev Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31558838 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ahmed D, and Cassol E (2017). Role of cellular metabolism in regulating type I interferon responses: Implications for tumour immunology and treatment. Cancer Lett. 409, 20–29. - PubMed
-
- Besser MJ, Shapira-Frommer R, Treves AJ, Zippel D, Itzhaki O, Hersh-kovitz L, Levy D, Kubi A, Hovav E, Chermoshniuk N, et al. (2010). Clinical responses in a phase II study using adoptive transfer of short-term cultured tumor infiltration lymphocytes in metastatic melanoma patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 16, 2646–2655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

