Microglial UCP2 Mediates Inflammation and Obesity Induced by High-Fat Feeding
- PMID: 31495690
- PMCID: PMC7251564
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.08.010
Microglial UCP2 Mediates Inflammation and Obesity Induced by High-Fat Feeding
Abstract
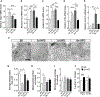
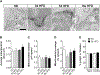
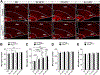
Microglia play a crucial role in immune responses, including inflammation. Diet-induced obesity (DIO) triggers microglia activation and hypothalamic inflammation as early as 3 days after high-fat diet (HFD) exposure, before changes in body weight occur. The intracellular mechanism(s) responsible for HFD-induced microglia activation is ill defined. Here, we show that in vivo, HFD induced a rapid and transient increase in uncoupling protein 2 (Ucp2) mRNA expression together with changes in mitochondrial dynamics. Selective microglial deletion of Ucp2 prevented changes in mitochondrial dynamics and function, microglia activation, and hypothalamic inflammation. In association with these, male and female mice were protected from HFD-induced obesity, showing decreased feeding and increased energy expenditure that were associated with changes in the synaptic input organization and activation of the anorexigenic hypothalamic POMC neurons and astrogliosis. Together, our data point to a fuel-availability-driven mitochondrial mechanism as a major player of microglia activation in the central regulation of DIO.
Keywords: POMC; diet-induced obesity; hypothalamus; metabolism; microglia; mitochondrial dynamics; mitochondrial respiration; neuroinflammation; synaptic plasticity.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
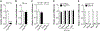

References
-
- Arsenijevic D, Onuma H, Pecqueur C, Raimbault S, Manning BS, Miroux B, Couplan E, Alves-Guerra MC, Goubern M, Surwit R, et al. (2000). Disruption of the uncoupling protein-2 gene in mice reveals a role in immunity and reactive oxygen species production. Nat. Genet 26, 435–439. - PubMed
-
- Arsenijevic D, Clavel S, Sanchis D, Plamondon J, Huang Q, Ricquier D, Rouger L, and Richard D (2007). Induction of Ucp2 expression in brain phagocytes and neurons following murine toxoplasmosis: an essential role of IFN-gamma and an association with negative energy balance. J. Neuroimmunol 186, 121–132. - PubMed
-
- Bouillaud F (2009). UCP2, not a physiologically relevant uncoupler but a glucose sparing switch impacting ROS production and glucose sensing. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1787, 377–383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

