Potential of circulating pro-angiogenic microRNA expressions as biomarkers for rapid angiographic stenotic progression and restenosis risks in coronary artery disease patients underwent percutaneous coronary intervention
- PMID: 31495986
- PMCID: PMC6977144
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23013
Potential of circulating pro-angiogenic microRNA expressions as biomarkers for rapid angiographic stenotic progression and restenosis risks in coronary artery disease patients underwent percutaneous coronary intervention
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate the correlation of pro-angiogenic microRNA (miRNA) expressions with rapid angiographic stenotic progression (RASP) and restenosis risks in coronary artery disease (CAD) patients underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with drug-eluting stents (DES).
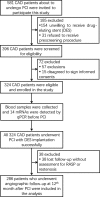
Methods: A total of 286 CAD patients underwent PCI with DES were consecutively recruited in this study. Plasma samples were collected before PCI operation, and 14 pro-angiogenic miRNAs were measured by real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Rapid angiographic stenotic progression at nontarget lesions and restenosis at stented lesions were evaluated by quantitative coronary angiography at 12 months after PCI operation.
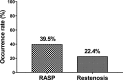
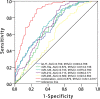
Results: The occurrence rates of RASP and restenosis were 39.5% and 22.4%, respectively. Let-7f, miR-19a, miR-19b-1, miR-92a, miR-126, miR-210, and miR-296 were decreased in RASP patients than non-RASP patients, among which let-7f, miR-19a, miR-126, miR-210, and miR-296 independently correlated with lower RASP occurrence by multivariate analysis, followed by receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve exhibited that these five miRNAs showed great value in predicting RASP risk with area under curve (AUC) 0.879 (95% CI: 0.841-0.917). Besides, let-7f, miR-19a, miR-92a, miR-126, miR-130a, and miR-210 were reduced in restenosis patients than non-restenosis patients, among them miR-19a, miR-126, miR-210, and miR-378 independently correlated with lower restenosis occurrence by multivariate analysis, followed by ROC curve disclosed that these four miRNAs had good value in predicting restenosis risk with AUC 0.776 (95% CI: 0.722-0.831).
Conclusions: Circulating let-7f, miR-19a, miR-126, miR-210, and miR-296 independently correlate with reduced RASP risk, while miR-19a, miR-126, miR-210, and miR-378 independently correlate with decreased restenosis risk in CAD patients underwent PCI with DES.
Keywords: coronary artery disease; percutaneous coronary intervention; pro-angiogenesis microRNA; rapid angiographic stenotic progression; restenosis.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Mack M, Gopal A. Epidemiology, traditional and novel risk factors in coronary artery disease. Heart Failure Clin. 2016;12(1):1‐10. - PubMed
-
- Hata J, Kiyohara Y. Epidemiology of stroke and coronary artery disease in Asia. Circ J. 2013;77(8):1923‐1932. - PubMed
-
- Stanik‐Hutt JA. Drug‐coated stents: preventing restenosis in coronary artery disease. J Cardiovas Nurs. 2004;19(6):404‐408. - PubMed
-
- Levine GN, Bates ER, Blankenship JC, et al. A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58(24):e44‐e122. - PubMed
-
- Vassiliades TA, Douglas JS, Morris DC, et al. Integrated coronary revascularization with drug‐eluting stents: immediate and seven‐month outcome. J Thoracic Cardiovas Surg. 2006;131(5):956‐962. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

