Noninvasive Mapping of the Electrophysiological Substrate in Cardiac Amyloidosis and Its Relationship to Structural Abnormalities
- PMID: 31496332
- PMCID: PMC6818012
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012097
Noninvasive Mapping of the Electrophysiological Substrate in Cardiac Amyloidosis and Its Relationship to Structural Abnormalities
Abstract
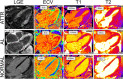
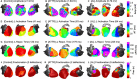
Background The relationship between structural pathology and electrophysiological substrate in cardiac amyloidosis is unclear. Differences between light-chain (AL) and transthyretin (ATTR) cardiac amyloidosis may have prognostic implications. Methods and Results ECG imaging and cardiac magnetic resonance studies were conducted in 21 cardiac amyloidosis patients (11 AL and 10 ATTR). Healthy volunteers were included as controls. With respect to ATTR, AL patients had lower amyloid volume (51.0/37.7 versus 73.7/16.4 mL, P=0.04), lower myocardial cell volume (42.6/19.1 versus 58.5/17.2 mL, P=0.021), and higher T1 (1172/64 versus 1109/80 ms, P=0.022) and T2 (53.4/2.9 versus 50.0/3.1 ms, P=0.003). ECG imaging revealed differences between cardiac amyloidosis and control patients in virtually all conduction-repolarization parameters. With respect to ATTR, AL patients had lower epicardial signal amplitude (1.07/0.46 versus 1.83/1.26 mV, P=0.026), greater epicardial signal fractionation (P=0.019), and slightly higher dispersion of repolarization (187.6/65 versus 158.3/40 ms, P=0.062). No significant difference between AL and ATTR patients was found using the standard 12-lead ECG. T1 correlated with epicardial signal amplitude (cc=-0.78), and extracellular volume with epicardial signal fractionation (cc=0.48) and repolarization time (cc=0.43). Univariate models based on single features from both cardiac magnetic resonance and ECG imaging classified AL and ATTR patients with an accuracy of 70% to 80%. Conclusions In this exploratory study cardiac amyloidosis was associated with ventricular conduction and repolarization abnormalities, which were more pronounced in AL than in ATTR. Combined ECG imaging-cardiac magnetic resonance analysis supports the hypothesis that additional mechanisms beyond infiltration may contribute to myocardial damage in AL amyloidosis. Further studies are needed to assess the clinical impact of this approach.
Keywords: T1 mapping; amyloid; arrhythmia; electrophysiology mapping; imaging.
Figures



References
-
- Kristen AV, Dengler TJ, Hegenbart U, Schonland SO, Goldschmidt H, Sack FU, Voss F, Becker R, Katus HA, Bauer A. Prophylactic implantation of cardioverter‐defibrillator in patients with severe cardiac amyloidosis and high risk for sudden cardiac death. Heart Rhythm. 2008;5:235–240. - PubMed
-
- Sayed RH, Rogers D, Khan F, Wechalekar AD, Lachmann HJ, Fontana M, Mahmood S, Sachchithanantham S, Patel K, Hawkins PN, Whelan CJ, Gillmore JD. A study of implanted cardiac rhythm recorders in advanced cardiac AL amyloidosis. Eur Heart J. 2015;36:1098–1105. - PubMed
-
- Gertz MA, Benson MD, Dyck PJ, Grogan M, Coelho T, Cruz M, Berk JL, Plante‐Bordeneuve V, Schmidt HHJ, Merlini G. Diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy of transthyretin amyloidosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;66:2451–2466. - PubMed
-
- Falk RH, Alexander KM, Liao R, Dorbala S. AL (light‐chain) cardiac amyloidosis: a review of diagnosis and therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68:1323–1341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

