HCN channel-mediated neuromodulation can control action potential velocity and fidelity in central axons
- PMID: 31496517
- PMCID: PMC6733576
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.42766
HCN channel-mediated neuromodulation can control action potential velocity and fidelity in central axons
Abstract
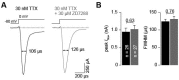
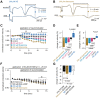
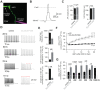
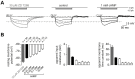
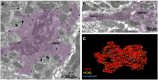
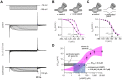
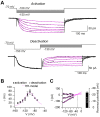
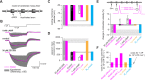
Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic-nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels control electrical rhythmicity and excitability in the heart and brain, but the function of HCN channels at the subcellular level in axons remains poorly understood. Here, we show that the action potential conduction velocity in both myelinated and unmyelinated central axons can be bidirectionally modulated by a HCN channel blocker, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), and neuromodulators. Recordings from mouse cerebellar mossy fiber boutons show that HCN channels ensure reliable high-frequency firing and are strongly modulated by cAMP (EC50 40 µM; estimated endogenous cAMP concentration 13 µM). In addition, immunogold-electron microscopy revealed HCN2 as the dominating subunit in cerebellar mossy fibers. Computational modeling indicated that HCN2 channels control conduction velocity primarily by altering the resting membrane potential and are associated with significant metabolic costs. These results suggest that the cAMP-HCN pathway provides neuromodulators with an opportunity to finely tune energy consumption and temporal delays across axons in the brain.
Keywords: HCN; axon; conduction velocity; mouse; neuromodulation; neuroscience.
© 2019, Byczkowicz et al.
Conflict of interest statement
NB, AE, JM, AT, JH, MK, RS, SH No competing interests declared
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

