The nature of the animacy organization in human ventral temporal cortex
- PMID: 31496518
- PMCID: PMC6733573
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.47142
The nature of the animacy organization in human ventral temporal cortex
Abstract
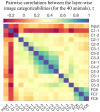
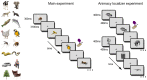
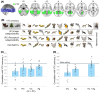
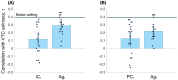
The principles underlying the animacy organization of the ventral temporal cortex (VTC) remain hotly debated, with recent evidence pointing to an animacy continuum rather than a dichotomy. What drives this continuum? According to the visual categorization hypothesis, the continuum reflects the degree to which animals contain animal-diagnostic features. By contrast, the agency hypothesis posits that the continuum reflects the degree to which animals are perceived as (social) agents. Here, we tested both hypotheses with a stimulus set in which visual categorizability and agency were dissociated based on representations in convolutional neural networks and behavioral experiments. Using fMRI, we found that visual categorizability and agency explained independent components of the animacy continuum in VTC. Modeled together, they fully explained the animacy continuum. Finally, clusters explained by visual categorizability were localized posterior to clusters explained by agency. These results show that multiple organizing principles, including agency, underlie the animacy continuum in VTC.
Keywords: animacy organization; human; neuroimaging; neuroscience; object categorization; object representation; visual cortex.
© 2019, Thorat et al.
Conflict of interest statement
ST, DP, MP No competing interests declared
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Ventral Visual Pathway Represents Animal Appearance over Animacy, Unlike Human Behavior and Deep Neural Networks.J Neurosci. 2019 Aug 14;39(33):6513-6525. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1714-18.2019. Epub 2019 Jun 13. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31196934 Free PMC article.
-
Untangling the Animacy Organization of Occipitotemporal Cortex.J Neurosci. 2021 Aug 18;41(33):7103-7119. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2628-20.2021. Epub 2021 Jul 6. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34230104 Free PMC article.
-
fMRI-adaptation and category selectivity in human ventral temporal cortex: regional differences across time scales.J Neurophysiol. 2010 Jun;103(6):3349-65. doi: 10.1152/jn.01108.2009. Epub 2010 Apr 7. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20375251 Free PMC article.
-
The functional architecture of the ventral temporal cortex and its role in categorization.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014 Aug;15(8):536-48. doi: 10.1038/nrn3747. Epub 2014 Jun 25. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24962370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low-level properties of natural images predict topographic patterns of neural response in the ventral visual pathway.J Vis. 2015;15(7):3. doi: 10.1167/15.7.3. J Vis. 2015. PMID: 26024512 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Face shape processing via visual-to-auditory sensory substitution activates regions within the face processing networks in the absence of visual experience.Front Neurosci. 2022 Oct 3;16:921321. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.921321. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36263367 Free PMC article.
-
A compositional neural code in high-level visual cortex can explain jumbled word reading.Elife. 2020 May 5;9:e54846. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54846. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32369017 Free PMC article.
-
Conceptual Associations Generate Sensory Predictions.J Neurosci. 2023 May 17;43(20):3733-3742. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1874-22.2023. Epub 2023 Apr 14. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37059461 Free PMC article.
-
Neural representation of abstract task structure during generalization.Elife. 2021 Mar 17;10:e63226. doi: 10.7554/eLife.63226. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33729156 Free PMC article.
-
Mid-level Feature Differences Support Early Animacy and Object Size Distinctions: Evidence from Electroencephalography Decoding.J Cogn Neurosci. 2022 Aug 1;34(9):1670-1680. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_01883. J Cogn Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35704550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baldassi C, Alemi-Neissi A, Pagan M, Dicarlo JJ, Zecchina R, Zoccolan D. Shape similarity, better than semantic membership, accounts for the structure of visual object representations in a population of monkey inferotemporal neurons. PLOS Computational Biology. 2013;9:e1003167. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003167. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

