High expression of APC is an unfavorable prognostic biomarker in T4 gastric cancer patients
- PMID: 31496624
- PMCID: PMC6710185
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i31.4452
High expression of APC is an unfavorable prognostic biomarker in T4 gastric cancer patients
Abstract
Background: Adenoma polyposis coli (APC) mutation is associated with tumorigenesis via the Wnt signaling pathway.
Aim: To investigate the clinical features and mechanism of APC expression in gastric cancer (GC).
Methods: Based on APC expression profile, the related genome-wide mRNA expression, microRNA (miRNA) expression, and methylation profile in GC, the relationship between APC and GC, as well as the prognostic significance of APC were systematically analyzed by multi-dimensional methods.
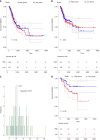
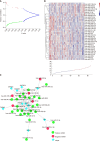
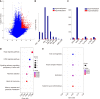
Results: We found that high expression of APC (APC high) was significantly associated with adverse outcomes of T4 GC patients. Genome-wide gene expression analysis revealed that varying APC expression levels in GC were associated with some important oncogenes, and corresponding cellular functional pathways. Genome-wide miRNA expression analysis indicated that most of miRNAs associated with high APC expression were downregulated. The mRNA-miRNA regulatory network analysis revealed that down-regulated miRNAs affected their inhibitory effect on tumor genes. Genome-wide methylation profiles associated with APC expression showed that there was differential methylation between the APC high and APC low groups. The number of hypermethylation sites was larger than that of hypomethylation sites, and most of hypermethylation sites were enriched in CpG islands.
Conclusion: Our research demonstrated that high APC expression is an unfavorable prognostic factor for T4 GC patients and may be used as a novel biomarker for pathogenesis research, diagnosis, and treatment of GC.
Keywords: Adenoma polyposis coli; Gastric cancer; Methylation; Prognosis; mRNA; miRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hypermethylation of adenomatous polyposis coli gene promoter is associated with novel Wnt signaling pathway in gastric adenomas.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012 Oct;27(10):1629-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2012.07219.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 22741528
-
miRNA-192 and -215 activate Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in gastric cancer via APC.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Sep;235(9):6218-6229. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29550. Epub 2020 Feb 24. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32091625
-
Prognostic impact of expression and methylation status of DENN/MADD domain-containing protein 2D in gastric cancer.Gastric Cancer. 2015 Apr;18(2):288-96. doi: 10.1007/s10120-014-0372-0. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Gastric Cancer. 2015. PMID: 24695972
-
MiRNA as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for gastric cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Aug 14;20(30):10432-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10432. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25132759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene methylation in gastric cancer.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Sep 23;424:53-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 May 10. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23669186 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinicopathological characteristics, survival outcomes, and genetic alterations of younger patients with gastric cancer: Results from the China National Cancer Center and cBioPortal datasets.Cancer Med. 2022 Aug;11(16):3057-3073. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4669. Epub 2022 Mar 22. Cancer Med. 2022. PMID: 35486034 Free PMC article.
-
To Identify Adenomatous Polyposis Coli Gene Mutation as a Predictive Marker of Endometrial Cancer Immunotherapy.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jul 22;10:935650. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.935650. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35938175 Free PMC article.
-
A pan-cancer analysis on the carcinogenic effect of human adenomatous polyposis coli.PLoS One. 2022 Mar 18;17(3):e0265655. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265655. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35303016 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically engineered mouse models in gastric precancerous lesions research.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2025 Jul 27;17(7):107610. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i7.107610. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2025. PMID: 40740928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment of a 5-gene risk model related to regulatory T cells for predicting gastric cancer prognosis.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Sep 3;20:433. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01502-6. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32908454 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–132. - PubMed
-
- Saito T, Kurokawa Y, Takiguchi S, Miyazaki Y, Takahashi T, Yamasaki M, Miyata H, Nakajima K, Mori M, Doki Y. Accuracy of multidetector-row CT in diagnosing lymph node metastasis in patients with gastric cancer. Eur Radiol. 2015;25:368–374. - PubMed
-
- Chen WQ, Li H, Sun KX, Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Zeng HM, Zou XN, Gu XY, He J. Report of Cancer Incidence and Mortality in China, 2014. Zhonghua Zhongliu Zazhi. 2018;40:5–13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

