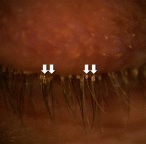
In vitro demodicidal activity of commercial lid hygiene products
- PMID: 31496640
- PMCID: PMC6689564
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S209067
In vitro demodicidal activity of commercial lid hygiene products
Abstract
Purpose: Demodex folliculorum is a ubiquitous mite that can infest the eyelash follicles. Two commercial lid hygiene products have asserted their effectiveness in killing Demodex mites, yet there has never been a comparative trial between these two products. This study evaluated the demodicidal activity of 0.01% hypochlorous acid (HOCl) solution (Avenova; NovaBay Pharmaceuticals; Emeryville, CA) and 4% terpinen-4-ol (T4O) solution (Cliradex, Bio-Tissue; Miami, FL) in comparison to mineral oil (MO), a negative control.
Methods: Live Demodex mites were obtained from volunteers. Samples were immersed in 1-2 drops of test solution: 0.01% HOCl, 4% T4O, or 100% MO. Samples were observed under the microscope every 10 mins for up to 90 mins. Kill time was defined as the elapsed time between the addition of test solution and all cessation of movement of the body, legs, mouth and pedipalps for a minimum of 60 seconds.
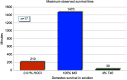
Results: T4O demonstrated a mean kill time of 40±0.0 mins. HOCl had a mean kill time of 87.86±4.23 mins, with 79% of samples surviving the full 90 mins. In the MO group, all samples survived through the 90 min mark. Kill time was statistically significant in favor of T4O as compared to HOCl (p=0.0005). There was no statistically significant difference in kill time between HOCl and MO (p=0.25).
Conclusion: 4% T4O effectively killed all adult mite samples within 40 mins of exposure. In contrast, the demodicidal activity of 0.01% HOCl was minimal, and comparatively similar to 100% MO.
Keywords: Demodex; blepharitis; hypochlorous acid; lid hygiene; tea tree oil; terpinen-4-ol.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Alan G Kabat is a consultant for Bio-Tissue, Inc. Dr Alan G Kabat reports non-financial support from TissueTech, Inc., during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Avellino Labs, Bio-Tissue, Inc., Bruder Healthcare Company, Inc., Lacrivera, OCuSOFT, Inc., Shire, Sight Sciences, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Vmax Vision, Kala Pharmaceuticals, Inc., National Vision Administrators, LLC, Quidel, TearScience and EyeGate Pharma, outside the submitted work. The author reports no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-Demodex Effect of Commercial Eyelid Hygiene Products.Semin Ophthalmol. 2021 Nov 17;36(8):719-722. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2021.1897859. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Semin Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33689584
-
Successful management of chronic Blepharo-rosacea associated demodex by lid scrub with terpinen-4-ol.Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2021 Jul 22;23:101171. doi: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2021.101171. eCollection 2021 Sep. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34368495 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro anti-demodectic effects and terpinen-4-ol content of commercial eyelid cleansers.Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2018 Dec;41(6):513-517. doi: 10.1016/j.clae.2018.08.003. Epub 2018 Aug 14. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2018. PMID: 30120003 Clinical Trial.
-
Recent advances on ocular Demodex infestation.Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2015 Jul;26(4):295-300. doi: 10.1097/ICU.0000000000000168. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 26058028 Review.
-
Can the tea tree oil (Australian native plant: Melaleuca alternifolia Cheel) be an alternative treatment for human demodicosis on skin?Parasitology. 2018 Oct;145(12):1510-1520. doi: 10.1017/S0031182018000495. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Parasitology. 2018. PMID: 29667560 Review.
Cited by
-
TFOS Lifestyle: Impact of cosmetics on the ocular surface.Ocul Surf. 2023 Jul;29:77-130. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2023.04.005. Epub 2023 Apr 13. Ocul Surf. 2023. PMID: 37061220 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of ocular Demodex infestation with topical ivermectin cream.Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2022 Apr 21;26:101551. doi: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2022.101551. eCollection 2022 Jun. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35509284 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the Surface: Understanding Demodex and Its Link to Blepharitis and Facial Dermatoses.Clin Ophthalmol. 2024 Jun 24;18:1801-1810. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S440199. eCollection 2024. Clin Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38948346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiparasitic Activity of Tea Tree Oil (TTO) and Its Components against Medically Important Ectoparasites: A Systematic Review.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jul 29;14(8):1587. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081587. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36015213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Pathogenic Role of Demodex Mites in Rosacea: A Potential Therapeutic Target Already in Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea?Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020 Dec;10(6):1229-1253. doi: 10.1007/s13555-020-00458-9. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2020. PMID: 33095403 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Czepita D, Kuźna-Grygiel W, Kosik-Bogacka D. Investigations on the occurrence as well as the role of Demodex folliculorum and Demodex brevis in the pathogenesis of blepharitis. Klin Oczna. 2005;107(1–3):80–82. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources