Extreme desert dust storms and COPD morbidity on the island of Crete
- PMID: 31496675
- PMCID: PMC6689762
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S208108
Extreme desert dust storms and COPD morbidity on the island of Crete
Abstract
Introduction and objectives: Short-term extreme increases in desert-derived particulate-matter with aerodynamic diameter below 10 μm (PM10) may affect emergency department (ED) visits due to COPD exacerbations.
Research question: Our aim was to identify the effect of extreme increases in desert-derived PM10 on ED visits for dyspnea and COPD exacerbations and on the related hospital admissions.
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of dyspnea-related ED visits and hospital admissions in Heraklion, Crete, during four consecutive storms of desert-derived PM10 that happened during March 2018. We collected data from over 17,000 ED visits and recorded patients with atopic symptoms, COPD exacerbations, and dyspnea, as well as admissions to the departments of pulmonary medicine, internal medicine, and cardiology. PM10 data were collected from a monitoring station in the same geographic area.
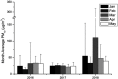
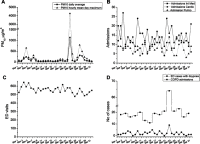
Results: Four desert dust storms were recorded during the study period with 238, 203, 1138, and 310 μg/m3 average-daily PM10 and 652, 308, 4262, and 778 μg/m3 hourly mean day-peak PM10, respectively. There was no clinically important increase in total ED visits, total admissions or admissions to the departments of cardiology, pulmonary medicine, or internal medicine, during PM10 peaks. However, during the desert dust storm with daily-average PM10 above 500 μg/m3, there was a striking increase in dyspnea-related ED visits (including COPD exacerbations, 3.6-fold increase), while there was no clinically important increase in non-asthma allergy-related ED visits.
Conclusion: Extreme desert dust storm episodes may cause meaningful increases in ED visits for dyspnea and COPD exacerbations/admissions.
Keywords: COPD; desert dust storms; emergency department overcrowding; particulate-matter.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Gerasopoulos E, Kouvarakis G, Babasakalis P, Vrekoussis M, Putaud JP, Mihalopoulos N. Origin and variability of particulate matter (PM10) mass concentrations over the Eastern Mediterranean. Atmos Environ. 2006;40(25):4679–4690. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.04.020 PubMed PMID: WOS:000239820600004. English. - DOI
-
- Vodonos A, Friger M, Katra I, et al. The impact of desert dust exposures on hospitalizations due to exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Air Qual Atmos Health. 2014;7(4):433–439. doi:10.1007/s11869-014-0253-z PubMed PMID: WOS:000345393400004. English. - DOI
-
- Stafoggia M, Zauli-Sajani S, Pey J, et al. Desert dust outbreaks in Southern Europe: contribution to daily PM(1)(0) concentrations and short-term associations with mortality and hospital admissions. Environ Health Perspect. 2016;124(4):413–419. doi:10.1289/ehp.1409164 PubMed PMID: 26219103. Pubmed Central PMCID: 4829979. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

