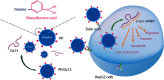
Inhibition of proliferation and migration of tumor cells through phenylboronic acid-functionalized polyamidoamine-mediated delivery of a therapeutic DNAzyme Dz13
- PMID: 31496692
- PMCID: PMC6691943
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S211744
Inhibition of proliferation and migration of tumor cells through phenylboronic acid-functionalized polyamidoamine-mediated delivery of a therapeutic DNAzyme Dz13
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Inhibition of Proliferation and Migration of Tumor Cells Through Phenylboronic Acid-Functionalized Polyamidoamine-Mediated Delivery of a Therapeutic DNAzyme Dz13 [Corrigendum].Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Dec 16;16:8117-8119. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S353250. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34949920 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The phenylboronic acid-functionalized polyamidoamine (PP) was employed as a gene carrier for Dz13 delivery, inducing an obvious anticancer response.
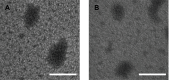
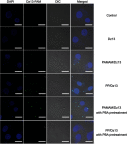
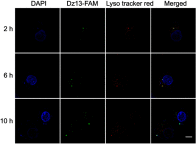
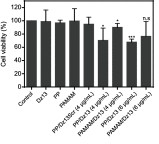
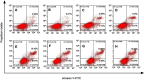
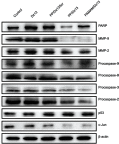
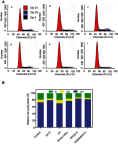
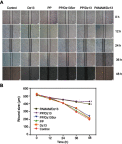
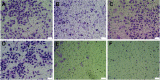
Materials and methods: The Dz13 condensation ability of PP was evaluated through gel retardation assay. The cellular uptake mechanism of PP/Dz13 nanoparticles was studied using confocal laser scanning microscope and flow cytometer. The inhibition ability of cell proliferation, migration and invasion was investigated through MTT assay, flow cytometry, wound healing and Transwell migration assays, using hepatocarcinoma cell line HepG2 as a model. Finally, Western blotting analysis was used to detect the signaling pathway associated with the inhibition of cell apoptosis and migration induced by Dz13 delivery.
Results: The carrier PP could efficiently condense Dz13 into stable nanoparticles at mass ratios of >1.5. The hydrodynamic diameter and zeta potential of PP/Dz13 nanoparticles were measured to be 204.77 nm and +22.00 mV at a mass ratio of 10.0, respectively. The nanoparticles could realize an efficient cellular uptake in sialic acid-dependent endocytosis manner. Moreover, the nanoparticles exhibited an obvious antiproliferation effect through the induction of cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest due to the cleavage of c-Jun mRNA. Besides, the suppression of cell migration and invasion could be achieved after the PP/Dz13 transfection, attributing to the decreased expression level of MMP-2 and MMP-9.
Conclusion: The PP provided a potential delivery system to achieve the tumor-targeting gene therapy.
Keywords: DNAzyme; antimigration effect; antiproliferation effect; gene therapy; phenylboronic acid; polyamidoamine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Liu CG, Han YH, Zhang JT, et al. Rerouting engineered metal-dependent shapes of mesoporous silica nanocontainers to biodegradable Janus-type (sphero-ellipsoid) nanoreactors for chemodynamic therapy. Chem Eng J. 2019;370:1188–1199. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.272 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

