Thermo-chemotherapy inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer cells via suppression of EIF5A2 expression
- PMID: 31496731
- PMCID: PMC6691964
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S215590
Thermo-chemotherapy inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer cells via suppression of EIF5A2 expression
Abstract
Purpose: Thermo-chemotherapy (TCT) is a new approach for the treatment of cancer that combines chemotherapy with thermotherapy. In the present study, we investigated the relationship between eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 (EIF5A2) and TCT sensitivity in gastric cancer (GC) to further illuminate the molecular mechanism underlying the effect of TCT on GC.
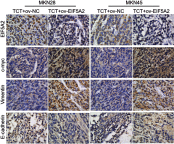
Methods: A TCT cell model was constructed, and EIF5A2 was silenced or overexpressed by infection with a lentivirus expressing either EIF5A2 or EIF5A2 shRNA. Then, RT-qPCR, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry assays were performed to evaluate the changes in the expression levels of EIF5A2, c-myc, vimentin, and E-cadherin. Cell proliferation and xenograft assays were conducted to evaluate the effect on cell proliferation. Finally, wound-healing and Transwell invasion assays were performed to evaluate the effects on migration and invasion.
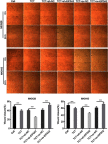
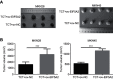
Results: TCT reduced EIF5A2 expression at both the mRNA and protein levels. It also inhibited cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, downregulated the expression of c-myc and vimentin, and increased the expression of E-cadherin in both MKN28 and MKN45 cells. Silencing of EIF5A2 enhanced the above effects of TCT on MKN28 and MKN45 cells, while overexpression of EIF5A2 had the opposite effects. In addition, EIF5A2 overexpression weakened the inhibitory effect of TCT on tumor growth in vivo as well as the effects on c-myc, vimentin, and E-cadherin.
Conclusion: TCT inhibits GC cell proliferation and metastasis by suppressing EIF5A2 expression. Our results provide new insights into our understanding of the molecular mechanism underlying the effects of TCT in GC.
Keywords: EIF5A2; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; gastric cancer; proliferation; thermo-chemotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest pertaining to this work.
Figures

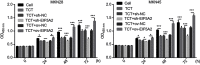


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

